Overview
- Peptide (C)KITHSPQAHDNPQEK, corresponding to amino acid residues 150-164 of human Ephrin-A1 (Accession P20827). Extracellular.
- Human Malme-3M melanoma cell lysate, mouse brain and rat heart membranes (1:200-1:1500).
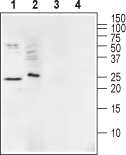 Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and human Malme-3M melanoma cell lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Ephrin-A1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-031), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and human Malme-3M melanoma cell lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Ephrin-A1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-031), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Ephrin-A1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Ephrin-A1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER031).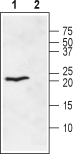 Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-Ephrin-A1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-031), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-Ephrin-A1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-031), (1:400).
2. Anti-Ephrin-A1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Ephrin-A1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER031).
- Rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells (1:50).
Ephrin-A1, a ligand of type-A Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and the Eph/ephrin system, has been shown to play important roles in the nervous system, tissue patterning and cell adhesion through receptor–ligand interactions and intracellular signaling1. Ephrins can be divided into two subclasses: ephrin A and ephrin B. Ephrin A ligands (ephrin A1-A5) are anchored to the cell surface via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor and bind to Eph A receptors (Eph A1-A8), whereas ephrin B ligands (ephrin B1-B3) have transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains and interact with Eph B receptors (Eph B1-B6)2.
Eph receptors and ephrins are highly expressed in the brain and in the developing nervous system, where they have well-known roles in the establishment of neuronal connectivity by guiding axons to the appropriate targets and regulating the formation of synaptic connections. Ephrins are expressed in numerous regions of the vertebrate embryo including the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm3.
Ephrin (Eph) receptors are frequently overexpressed in a variety of human malignant tumors, and are associated with tumor growth, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Recent studies using clinical samples showed that ephrin-A1 expression was up-regulated in colorectal cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma and positively correlated with a poor prognostic value4.
