Overview
- Peptide ((C)KQPDIKNPKLTKDQR, corresponding to amino acid residues 387 - 401 of rat FLRT3 (Accession B1H234). Extracellular, N-term.

FLRT3 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-FR053)
 Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-FLRT3 (extracellular) Antibody (#AFR-053), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-FLRT3 (extracellular) Antibody (#AFR-053), (1:200).
3-4. Anti-FLRT3 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with FLRT3 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-FR053). Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-FLRT3 (extracellular) Antibody (#AFR-053), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-FLRT3 (extracellular) Antibody (#AFR-053), (1:200).
3-4. Anti-FLRT3 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with FLRT3 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-FR053).
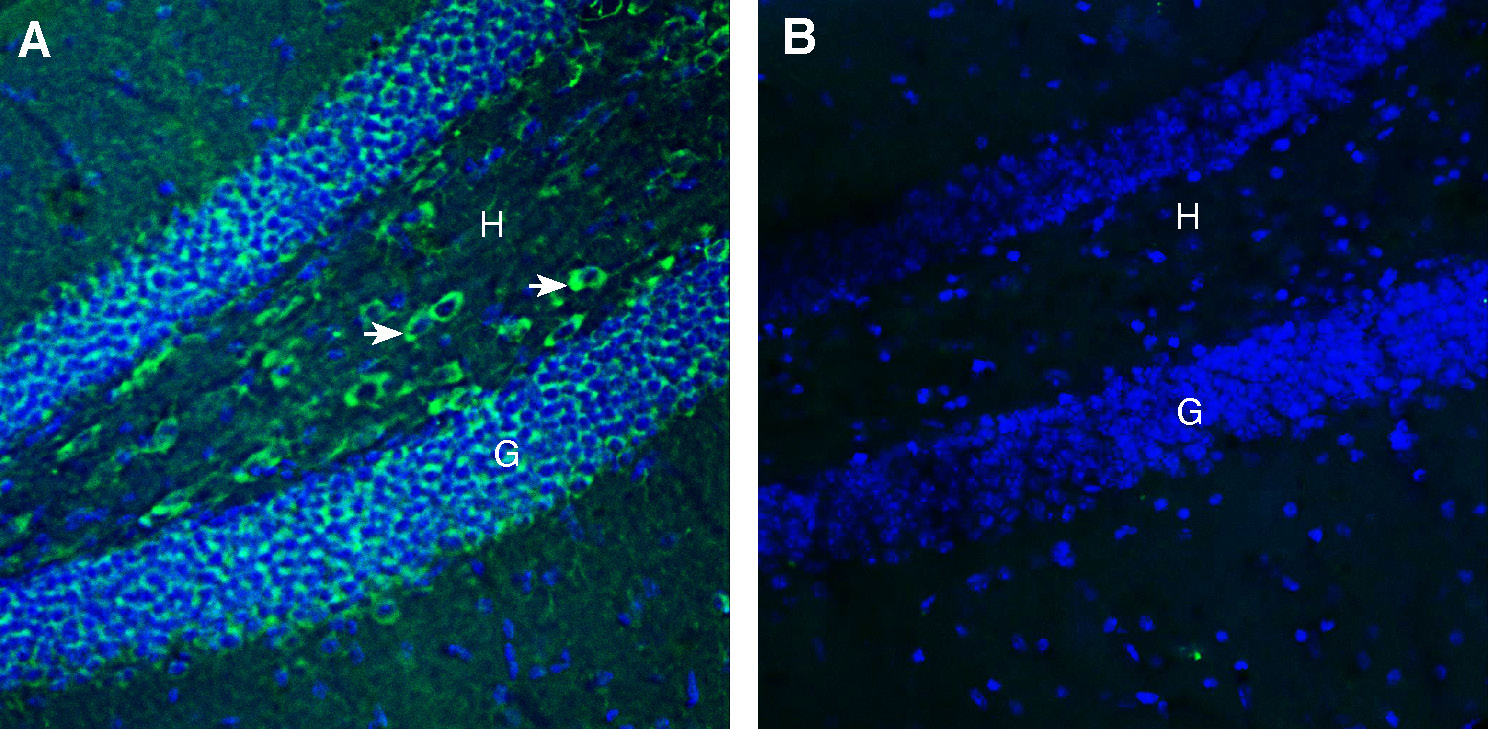 Expression of FLRT3 in mouse hippocampus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-FLRT3 (extracellular) Antibody (#AFR-053), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Staining in the hippocampal dentate gyrus region, showed immunoreactivity (green) in the granule layer (G) and in the hilus (H, arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with FLRT3 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-FR053), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of FLRT3 in mouse hippocampus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-FLRT3 (extracellular) Antibody (#AFR-053), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Staining in the hippocampal dentate gyrus region, showed immunoreactivity (green) in the granule layer (G) and in the hilus (H, arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with FLRT3 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-FR053), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Expression of FLRT3 in mouse cerebellum.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-FLRT3 (extracellular) Antibody (#AFR-053), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. FLRT3 immunoreactivity (green) appears in the purkinje cell layer (P, arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with FLRT3 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-FR053), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of FLRT3 in mouse cerebellum.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-FLRT3 (extracellular) Antibody (#AFR-053), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. FLRT3 immunoreactivity (green) appears in the purkinje cell layer (P, arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with FLRT3 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-FR053), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Soler-Llavina, G. J. et al. (2013) Neuron., 79, 439.
- Lacy, S. E. et al. (1999) Genomics., 62, 417.
- Maretto, S. et al. (2008) Dev. Biol., 318, 184.
- Hampel, F. et al. (2011) EMBO. J., 30, 2920.
- Fleitas, C. et al. (2021) J. Neurosci., 41, 7350.
The leucine-rich repeat (LRR) superfamily is a diverse protein family that consist of leucine-rich domains (LRR domains). The LRR domain is known to regulate protein-protein interaction or cell adhesion. A Large portion of LRR proteins mediate the differentiation and development of nervous tissues1.
The fibronectin leucine-rich transmembrane 3 (FLRT3) protein play an important function during excitatory neuron development including neuron migration, axon guidance, or synapse formation2. FLRT3 gene is encoding single pass transmembrane domain with one extracellular LRR domain and a juxtamembrane fibronectin type 3 (FNIII) module. It was found to be expressed in kidney, brain, pancreases, skeletal muscle, lungs, liver placenta and heart3.
FLRT3 display a unique multifunctional property acting as chemorepellent by binding to the Netrin receptor Unc5D and regulating radial migration of subventricular progenitors. In addition, it acts as homophilic adhesion molecule regulating the tangential dispersion of migrating neuron progenitors in the developing cortex4. FLRT3 knock out in mice leads to a variety of malformations, like disorganized basement membrane, failure of embryonic turning and ventral body closure, cardiac bifida and asymmetric development of headfolds5.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-FLRT3 (extracellular) Antibody (#AFR-053) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize FLRT3 from mouse, rat and human samples.

