Overview
- Peptide (C)ERNMHQMTDGLDK, corresponding to amino acids residues 194-206 of rat GAT-1 (Accession P23978). 2nd extracellular loop.

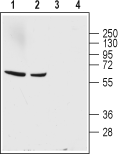 Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1,2. Anti-GABA Transporter 1 (GAT-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AGT-001), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1,2. Anti-GABA Transporter 1 (GAT-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AGT-001), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-GABA Transporter 1 (GAT-1) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GABA Transporter 1/GAT-1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GT001).
 Expression of GABATR in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat cerebellum using Anti-GABA Transporter 1 (GAT-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AGT-001), (1:200). A. GAT-1 staining is shown in green. B. Neurons expressing gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) were labeled with mouse Anti-parvalbumin (red). C. Merge of the two images demonstrates partial colocalization (arrows). GAT-1 appears both in the soma of Purkinje cells (vertical arrows) and in the pinceau (horizontal arrows).
Expression of GABATR in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat cerebellum using Anti-GABA Transporter 1 (GAT-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AGT-001), (1:200). A. GAT-1 staining is shown in green. B. Neurons expressing gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) were labeled with mouse Anti-parvalbumin (red). C. Merge of the two images demonstrates partial colocalization (arrows). GAT-1 appears both in the soma of Purkinje cells (vertical arrows) and in the pinceau (horizontal arrows).
- Gonzalez-Burgos, G. (2010) Adv. Pharmacol. 58, 175.
- Gether, U. et al. (2006) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 27, 375.
- Meinild, A.K. et al. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 16226.
- Conti, F. et al. (2011) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 5, 2.
- Lewis, D.A. et al. (2005) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6, 312.
- Fueta, Y. et al. (2003) Neuroscience 118, 371.
- Frahm, C. et al. (2004) NeuroReport 15, 9.
γ-Aminobutiric acid (GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. Transmission via GABA can be halted by its reuptake through GABA transporters (GATs). These membrane proteins belong to the super family of slc6 genes which encode transporters responsible for the uptake of dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, glycine and GABA in a Na+-dependent manner1,2.
To date, four GATs have been identified: GAT-1, GAT-2, GAT-3 and BGT-1. Like all members of the slc6 family, they have twelve transmembrane domains and short intracellular N- and C-termini1. GATs couple the transport of one GABA molecule to 2 Na+ ions and one Cl- ion3. GAT-1 activity can be regulated at the level of its plasma membrane expression which is in part regulated by its trafficking via phosphorylation of residues in intracellular loops1.
GAT-1 expression is restricted to the central nervous system, specifically to axon terminals, in the neocortex and in some astrocytic processes4.
GAT-1 may be implicated in various psychological and neurological disorders such as schizophrenia, epilepsy and cerebral ischemia1,5-7.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-GABA Transporter 1 (GAT-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AGT-001) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize GAT-1 from rat, mouse, and human samples.
Applications
Citations
- Rat brain lysate.
Moldavan, M. et al. (2017) J. Neurophysiol. 118, 3092.
- Human brain sections.
Fuhrer, T.E. et al. (2017) Neuroscience 351, 108.

