Overview
- Peptide QGESRRQEPGDFVKQ(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 29-43 of human GABRA3 (Accession P34903). Extracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat brain membranes (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-GABA(A) α3 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGA-003), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-GABA(A) α3 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGA-003), (1:200).
2. Anti-GABA(A) α3 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody preincubated with GABA(A) α3 Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GA003).
- Transfected COS-7 cells (1 µg antibody/140 µg lysate) (Zhou, C. et al. (2013) J. Biol. Chem. 288, 21458.).
- Rat brain frozen sections (1:200).
- Rat insulinoma cell line (1:50).
The neurotransmitter GABA (γ-aminobutiric acid) inhibits the activity of signal-receiving neurons by interacting with the GABAA receptor on these cells.1 Binding of GABA to its GABAA receptor results in conformational changes that open a Cl- channel, producing an increase in membrane conductance that results in inhibition of neural activity.2
There are two major types of GABA receptors: the ionotropic GABAA receptors (GABAAR) and the metabotropic GABAB receptors (GABABR). GABAARs belong to the ligand-gated ion channel superfamily.1,2
GABAARs are heteropentamers, in which all five subunits contribute to formation of the pore. Eight subunit isoforms have been cloned: α, β, γ, δ, ε, π, θ, and ρ.1 Six α subunits isoforms (α1-α6) have been shown to exist in mammals.
In most cases, the native GABAA receptors consist of 2α, 2β, and 1γ subunits.
The α3-subunit is highly expressed during development (along with α2 and α5) and then declines in adulthood, where the α1-subunit becomes predominant. The failure to complete this switch could be a major predispositional factor in the development of temporal lobe epilepsy.3
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
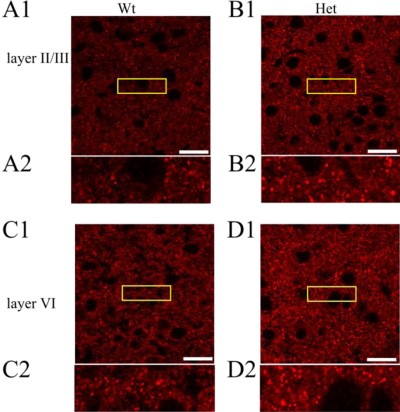
GABA(A) α3 Receptor expression increases in Heterozygous GABA(A) α1 Receptor knockout.Immunohistochemical staining of cortices from wild type (A and C) and Het α1 KO (B and D) mice in layers II/III (A and B) and VI (C and D) of the somatosensory cortex (white scale bar, 20 μm, n > 6) using Anti-GABA(A) α3 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGA-003). The yellow boxed areas are displayed on a magnified scale below each image (A2–D2).Adapted from Zhou, C. et al. (2013) with permission of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.

