Overview
- Peptide NSKDEKLSPENFTR(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 37-50 of rat GABRA4 with replacement of C44 with serine (Accession P28471). Extracellular, N-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain membrane (lanes 2 and 5) and human CCF-STGI Brain astrocytoma cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-GABA(A) α4 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGA-008), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain membrane (lanes 2 and 5) and human CCF-STGI Brain astrocytoma cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-GABA(A) α4 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGA-008), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-GABA(A) α4 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GABA(A) α4 Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GA008).
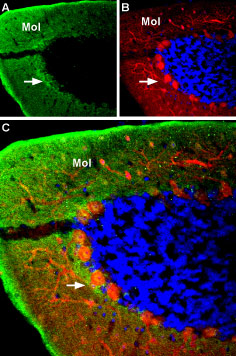 Expression of GABA(A) α4 Receptor in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat cerebellum using Anti-GABA(A) α4 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGA-008). A. GABRA4 staining (green) appears in the molecular layer (Mol) and around the soma of Purkinje cells (arrow). B. Parvalbumin (red), a marker of Purkinje and interneuronal cells, is stained in the same section. C. Merge of the images demonstrates expression of GABRA4 around the soma of Purkinje cells. DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
Expression of GABA(A) α4 Receptor in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat cerebellum using Anti-GABA(A) α4 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGA-008). A. GABRA4 staining (green) appears in the molecular layer (Mol) and around the soma of Purkinje cells (arrow). B. Parvalbumin (red), a marker of Purkinje and interneuronal cells, is stained in the same section. C. Merge of the images demonstrates expression of GABRA4 around the soma of Purkinje cells. DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
 Expression of GABA(A) α4 Receptor in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of GABA(A) α4 Receptor in intact living rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-GABA(A) α4 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGA-008), (1:50), (red). B. Merge of A with the live view of the cell.
Expression of GABA(A) α4 Receptor in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of GABA(A) α4 Receptor in intact living rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-GABA(A) α4 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGA-008), (1:50), (red). B. Merge of A with the live view of the cell.
- Owens, D.F. and Kriegstein, A.R. (2002) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 715.
- Whiting, P.J. (1999) Neurochem. Int. 34, 387.
- Mihic, S.J. and Harris, R.A. (1997) Alcohol Health Res. World 21, 127.
- Neelands, T.R. et al. (1999) J. Neurosci. 19, 7057.
- Olsen, R.W. and Tobbin, A.J. (1990) FASEB J. 4, 1469.
GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Its production, release, reuptake, and metabolism all occur in the nervous system1.
The GABA transmitter interacts with two major types of receptors: ionotropic GABAA receptors (GABAAR) and metabotropic GABAB receptors (GABABR).
GABAARs belong to the ligand-gated ion channel superfamily2. GABA inhibits the activity of signal-receiving neurons by interacting with the GABAA receptor on these cells3. Binding of GABA to its GABAA receptor results in conformational changes that open a Cl- channel, producing an increase in membrane conductance that results in inhibition of neural activity2.
GABAARs are heteropentamers, in which all five subunits contribute to the pore formation. To date, eight subunit isoforms have been cloned: α, β, γ, δ, ε, π, θ, and ρ1. Six α subunit isoforms have been found to exist in mammals (α1-α6). In most cases, native GABAA receptors consist of 2α, 2β, and 1γ subunits. The α subunit is the most common and is expressed ubiquitously. It determines the affinity of GABAARs for allosteric ligands.
Each subtype has a unique regional expression in the brain, and individual neurons often express multiple subtypes4. For example, the α4 subunit is detected in the hippocampus, cortex, olfactory bulb and in the basal forebrain5.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of rat GABA(A) α4 subunit. Anti-GABA(A) α4 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGA-008) can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and live cell imaging applications. It was designed to recognize GABRA4 from human, rat and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Mouse brain lysate (1:200).
Seo, S. and Leitch, B. (2015) Neuroscience 306, 28.
