Overview
- Peptide (C)DDNLVYHILRKHSAKR, corresponding to amino acid residues 192-207 of human GDNF (precursor) (Accession P39905). C-terminus of the mature GDNF.
- Recombinant human GDNF protein (1:1000).
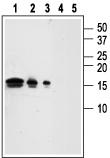 Western blot analysis of Recombinant human GDNF protein:Lanes 1, 4: 50 ng Recombinant human GDNF protein (#G-240).
Western blot analysis of Recombinant human GDNF protein:Lanes 1, 4: 50 ng Recombinant human GDNF protein (#G-240).
Lanes 2, 5: 10 ng Recombinant human GDNF protein.
Lanes 3, 4: 1 ng Recombinant human GDNF protein.
Lanes 1-3: Anti-GDNF Antibody (#ANT-014), (1:1000).
Lanes 4-5: Anti-GDNF Antibody, preincubated with GDNF Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NT014).
- Rat dorsal root ganglion sections (frozen) (1:100).
- Paraformaldehyde-fixed rat C6 glioma cells (1:200-1:500).
Glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a neurotrophic factor originally identified for its ability to promote the survival of dopaminergic neurons in the midbrain.1
GDNF is part of the neurotrophic factor family known as GDNF-family ligand (GFL), which includes neurturin (NRTN), artemin (ARTN), and persephin (PSPN).2,3 The GFL ligands are structurally related to the transforming growth factor-b (TGF-b) protein superfamily and contain seven cysteine residues with the same relative spacing as other members of this family.2
Typical of neurotrophic factors, GDNF is produced in the form of a precursor, preproGDNF, which is then cleaved during secretion to become proGDNF, and later processed to the mature (homodimeric) GDNF form.2
The GFLs convey their activity by binding to a multicomponent receptor that includes the RET receptor tyrosine kinase and a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked ligand-binding subunit known as GDNF family receptor α (GFRα).2,3 Four different GFRα subunits have been identified (GFRα 1-4) that determine the specificity of the GFRα-RET receptor complex. Thus, GFRα1 together with RET make up the high affinity receptor for GDNF.
The GDNF and GFRα complex interaction with RET induces activation of the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain of the latter. Phosphorylated RET can then interact with several intracellular signaling cascades including MAP kinase, PI3K and PLCγ signaling pathways.2,3
Lately a RET-independent signaling pathway for GDNF has been shown to involve binding of GDNF and GFRα to the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM). Signaling of GDNF via the NCAM complex stimulates intracellular tyrosine kinases such as Fyn and FAK.4
GDNF is synthesized and secreted by a wide variety of cell types in the central and peripheral nervous system where it exerts its neurotrophic effects in the development and maintenance of distinct sets of neurons. Accordingly, GDNF knockout mice die shortly after birth, reflecting the central role of GDNF in neurodevelopment.2
Remarkably, GDNF was found to be an essential morphogen for kidney formation as well as to have a role is spermatogenesis.3
