Overview
- Peptide (C)KYLYEDEG(S)WTRNS, corresponding to amino acid residues 288-301 of rat GLP1R (Accession P32301). 2nd extracellular loop.

 Western blot analysis of rat pancreas lysate (lanes 1 and 5), mouse preadipocyte 3T3-L1 lysate (lanes 2 and 6), rat pancreatic islet cell line RIN-5F lysate (lanes 3 and 7) and human pancreatic carcinoma PANC-1 lysate (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-GLP1R (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-021), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat pancreas lysate (lanes 1 and 5), mouse preadipocyte 3T3-L1 lysate (lanes 2 and 6), rat pancreatic islet cell line RIN-5F lysate (lanes 3 and 7) and human pancreatic carcinoma PANC-1 lysate (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-GLP1R (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-021), (1:200).
5-8. Anti-GLP1R (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GLP1R (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GR021).
 Expression of Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in rat pancreasImmunohistochemical staining of rat pancreas paraffin embedded sections using Anti-GLP1R (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-021), (1:100). Staining (brown color) is present in endocrine cells of the Isles of Langerhans. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
Expression of Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in rat pancreasImmunohistochemical staining of rat pancreas paraffin embedded sections using Anti-GLP1R (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-021), (1:100). Staining (brown color) is present in endocrine cells of the Isles of Langerhans. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.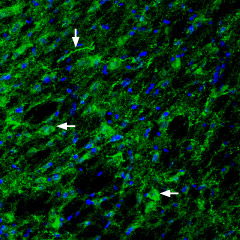 Expression of Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in rat hypothalamusImmunohistochemical staining of rat hypothalamus with Anti-GLP1R (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-021), (1:200). Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (green) appears in the lateral hypothalamic region axonal profiles (vertical arrow) and nerve cell profiles (horizontal arrows). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
Expression of Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in rat hypothalamusImmunohistochemical staining of rat hypothalamus with Anti-GLP1R (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-021), (1:200). Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (green) appears in the lateral hypothalamic region axonal profiles (vertical arrow) and nerve cell profiles (horizontal arrows). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
 Expression of Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in rat pancreatic islet cellsCell surface detection of Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in live intact rat RIN-5F pancreatic islet cells. A. Cells were stained with Anti-GLP1R (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-021), (1:100), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Cell nuclei were visualized with the membrane-permeable DNA dye Hoechst 33342 (blue staining). C. Live view of the cells.
Expression of Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in rat pancreatic islet cellsCell surface detection of Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in live intact rat RIN-5F pancreatic islet cells. A. Cells were stained with Anti-GLP1R (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-021), (1:100), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Cell nuclei were visualized with the membrane-permeable DNA dye Hoechst 33342 (blue staining). C. Live view of the cells.
- Donath, M.Y. et al. (2003) J. Mol. Med. 81, 455.
- Buteau, J. (2008) Diabetes Metab. 34, S73.
- Holst, J.J. (2007) Physiol. Rev. 87, 1409.
- Harkavyi, A. and Whitton, P.S. (2010) Br. J. Pharmacol. 159, 495.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is a hormone secreted by the intestine following a meal1. This hormone is known to enhance the secretion of insulin, important glucose blood level regulation2,3. In pancreatic β-cells, other than stimulating insulin secretion, GLP-1 action is also important for β-cell mass expansion2.
GLP-1 exerts its biological functions through Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1 receptor), a member of the G-protein coupled receptor superfamily. Like all members, this receptor spans the membrane seven times. GLP-1 receptor couples with Gs, thereby stimulating adenylate cyclase, consequently leading to an increase in cAMP2.
The receptor is expressed in various tissues, namely the pancreas, adipose tissue, muscle, heart, gastrointestinal tract and liver. GLP-1 receptor is also found in the central nervous system where it provides a neuroprotective effect4.
The glucagon-like peptide 1 system may serve as a therapeutic treatment in diabetes mellitus, in order to maintain β-cell mass expansion2. In addition, the receptor may serve as a therapy target in various neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease4.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-GLP1R (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-021) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, and live cell imaging applications. It has been designed to recognize GLP1R from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Rat β-cell lysate (1:1000).
Gleizes, C. et al. (2016) J. Cell. Mol. Med. 20, 231.
- Gao, H. et al. (2012) J. Nucl. Med. 53, 1960.

