Overview
- Peptide (C)KDFLNYTLEERLED, corresponding to amino acid residues 39-52 of rat Glucose Transporter 3 (Accession Q07647). 1st extracellular loop.
- Rat and mouse brain membranes (1:200-1:1000).
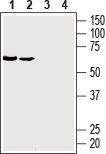 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-GLUT3 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGT-023), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-GLUT3 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGT-023), (1:400).
3, 4. Anti-GLUT3 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GLUT3 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GT023).
- Mouse brain sections (1:200).
- Mouse J774 macrophage cell line.
The GLUT protein family is encoded by the SLC2 genes and are a member of the major facilitator superfamily of membrane transporters. GLUTs are recognized as key regulators of whole-body glucose homeostasis, and are responsible for the uptake of carbohydrate-derived glucose by cells. There are 14 GLUT isoforms divided into 3 different group classes based on sequence similarity and structural and functional characteristics1,2.
GLUT3 is a low-Km protein responsible for glucose uptake into neurons. It is predominantly expressed in neurons and is commonly called “neuronal glucose transporter". The protein contains 12 membrane-spanning domains, an N-linked glycosylation site in loop 1 responsible for high-affinity transport of glucose, and intracellular NH2- and COOH- termini. In addition, there are several conserved residues and motifs designated “sugar transporter signatures”1,2.
GLUT3 levels are high in some malignant glioma cells compared to normal glial cells and therefore may be used as a therapeutic target in some cancer treatment3.
