Overview
- Peptide (C)KLTQSGPSNSSHVG, corresponding to amino acid residues 342 - 355 of rat GLUT8 (Accession Q9JJZ1). Extracellular, 5th loop.
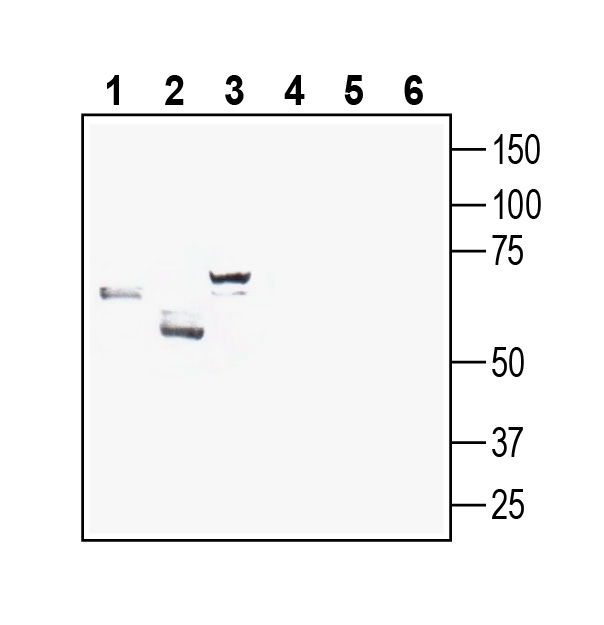 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse liver membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and mouse testis membranes (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-GLUT8 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGT-028), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse liver membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and mouse testis membranes (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-GLUT8 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGT-028), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-GLUT8 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GLUT8 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GT028).
The Glucose transporter (GLUT) family are transmembrane transporters encoded by the slc2a gene superfamily. They are responsible for the transportation of carbohydrates and other substrates down their concentration gradients across lipid bilayers. GLUT transporters therefore play a pivotal role in cellular energetics and glucose sensing. The GLUT family comprises 14 members, divided into 3 classes (I-III), with specific expression patterns and affinities for hexose sugars1.
GLUT8 is a class III glucose transporter predominantly expressed in testis and brain. It consists of 12 transmembrane domains, and a single N-glycosylation site. In heterologous expression systems, glucose transport activity was inhibited by fructose and galactose. The transporter carries an NH2-terminal endosomal/lysosomal targeting motif ([DE]XXXL[LI])2.
The in-vivo function of GLUT8 remains to be defined. Studies in slc2a8 knock-out mice showed a subtle phenotype including hypoactive sperm, hyperproliferation of hippocampal cells, and resistance to hepatosteatosis in mice fed with high fructose3.
