Overview
- Peptide (C)NNASLEQDQNH, corresponding to amino acid residues 3-13 of rat GnRHR (Accession P30969). Extracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat ovary and pituitary (1:200).
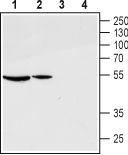 Western blot analysis of rat ovary (lanes 1 and 3) and pituitary (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-GnRH Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-030), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat ovary (lanes 1 and 3) and pituitary (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-GnRH Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-030), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-GnRH Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GnRH Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GR030).
- Rat ovary paraffin embedded sections (1:100).
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) or Luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH) is a decapeptide synthesized and released from neurons in the hypothalamus and stimulates the synthesis and release of gonadotropin hormone (or luteinizing hormone) and follicle stimulating hormone from the pituitary gland1. GnRH is expressed as various variants, and most vertebrates express more than one form of GnRH1-3.
GnRH and its variants bind and activate GnRH receptor (GnRHR), a member of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily. Three forms of the receptor have been identified in vertebrates (types I, II and III). Like all members, GnRHR has seven transmembrane domains and an extracellular N-terminus and an intracellular C-terminal tail. The receptor also has a number of glycosylation sites in its extracellular loops. In addition, the C-terminal tail is unusually short and lacks consensus sites known to undergo post-translational modifications like phosphorylation. In consequence, this affects the receptor’s desensitization and internalization4.
Expression of GnRHR is detected in the gonadotrope and various tissues like the breast, gonads, prostate and uterus4,5.
