Overview
- Peptide (C)DNYVHNWDWRFGG, corresponding to amino acid residues 82 - 94 of mouse HCAR2 (Accession Q9EP66). Extracellular, 1st loop.

Note: it is not expected to recognize the highly homologous human protein HCAR3 (Accession P49019). HCAR3 has no mouse or rat orthologs.
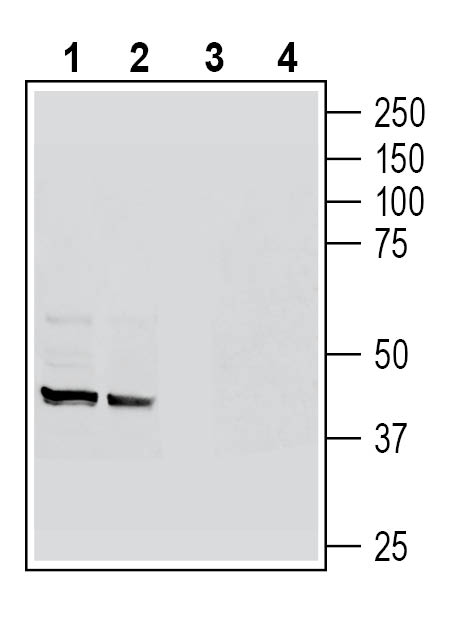 Western blot analysis of rat spleen lysates (lanes 1 and 3) and rat colon membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AHR-012), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat spleen lysates (lanes 1 and 3) and rat colon membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AHR-012), (1:200).
3-4. Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-HR012). Western blot analysis of mouse colon lysates (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse lung lysates (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AHR-012), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse colon lysates (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse lung lysates (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AHR-012), (1:200).
3-4. Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-HR012). Western blot analysis of human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysates (lanes 1 and 3) and human HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell line lysates (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AHR-012), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysates (lanes 1 and 3) and human HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell line lysates (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AHR-012), (1:200).
3-4. Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-HR012).
 Expression of GPR109A in rat cingulate cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AHR-012), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. GPR109A immunoreactivity (green) appears in outlines of cortical neurons (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-HR012), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of GPR109A in rat cingulate cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AHR-012), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. GPR109A immunoreactivity (green) appears in outlines of cortical neurons (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-HR012), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Ahmed K. (2011) Front. Endocrinol. 25, 51.
- Graff E. et al (2016) Metabolism. 65, 102-113.
- Offermanns S., (2017) Trends Endocrinol Metab. 28, 227-236.
- Offermanns S.,(2014) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 54, 407–34.
Hydroxy-carboxylic acid receptors (HCA1-3) are a family of G-protein-coupled receptors that regulate lipolysis. HCAR2 (GPR109A) was identified as the receptor for nicotinic acid (niacin; vitamin B3) and beta-hyroxybutyrate (β-OHB), a ketone body synthesized by the liver under negative energy balance1.
HCAR2 is mainly expressed on adipocytes and immune cells and in lower levels in retinal pigmented and colonic epithelial cells, microglia and normal mammary tissue. High levels of HCAR2 can be found in immune cells such as macrophages in response to the presence of interferon-γ, TNF-α and hypoxia2.
HCAR2 activity in adipocytes promotes inhibition of adenylate cyclase and decrease cAMP levels. HCAR2 activity leads to a rapid decrease in lipolysis and reduction in the release of fatty acids from the adipocytes3.
Activation of HCAR2 has also been associated with anti-inflammatory effects in different disease states such as sepsis, diabetes and obesity. Interaction of HCAR2 with niacin and β-OHB under this conditions lead to variety of signaling events involving inflammatory downstream targets4.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-GPR109A/HCAR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AHR-012) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize GPR109A from rat, mouse and human samples.

