Overview
- Peptide (C)APVHRDWRVHLALD, corresponding to amino acid residues 291 - 304 of mouse GPR142 (Accession Q7TQN9). Extracellular, 3rd loop.

 Western blot analysis of mouse pancreas lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat pancreas lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-082), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of mouse pancreas lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat pancreas lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-082), (1:400).
3-4. Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR142 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR082).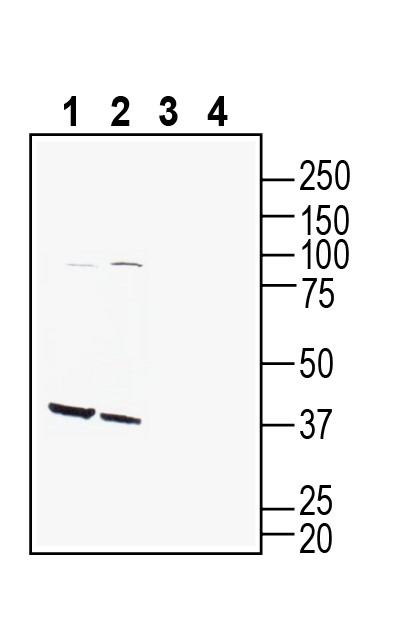 Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-082), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-082), (1:400).
3-4. Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR142 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR082). Western blot analysis of human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 4), human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-082), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 4), human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-082), (1:400).
4-6. Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR142 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR082).
 Expression of GPR142 in rat ventromedial hypothalamus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-082), (1:1000), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. GPR142 immunoreactivity (green) appears in glial processes (vertical arrow) and in cells lining the wall of 3rd ventricle (horizontal arrow). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with GPR142 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR082), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). 3rd V= 3rd ventricle.
Expression of GPR142 in rat ventromedial hypothalamus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-082), (1:1000), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. GPR142 immunoreactivity (green) appears in glial processes (vertical arrow) and in cells lining the wall of 3rd ventricle (horizontal arrow). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with GPR142 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR082), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). 3rd V= 3rd ventricle.
- Kamato, D. et al. (2015) Front. Cardiovasc. Med., 2, 14.
- Kaushik, C.A. et al. (2018) J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn., 36, 1788.
- Al-Amily, I.M. et al. (2019) Pflugers. Arch. – Eur. J. Physiol. 471, 633.
- Murakoshi, M. et al. (2017) Journal of Receptors and Signal Transduction, 37(3), 290-296.
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest family of membrane proteins and mediate a myriad of physiological and pathophysiological signaling processes. Of these receptors, all are seven membrane spanning receptors but not all are G protein binding but it is convenient to refer to the receptors as GPCRs1.
The GPR142 is a GPCR selectively activated by aromatic amino acids and share 33% amino acid identity with GPR139. L-tryptophan representing one of the most potent ligands, having an EC50 values of 0.2 – 1 mM2. GPR142 is expressed in both rodent and human pancreatic beta cells. Moreover, it was found to be implicated in the regulation of insulin, thereby having a crucial role in Type II diabetes management3.
Moreover, GPR142 is highly expressed in immune cells and its ligand L-tryptophan and metabolite serotonin are known to take part in inflammation process. It was shown that mice lacking GPR142 gene are more resilient to anti-type II collagen (CII) antibody-induced arthritis however the exact mechanism is currently unknown4.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-GPR142 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-082) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize GPR142 from rat, mouse and human samples.

