Overview
- Peptide (C)HNQLDLSNGSHPEEYK, corresponding to amino acid residues 7 - 22 of mouse GPR18 (Accession Q8K1Z6). Extracellular, N-terminus.
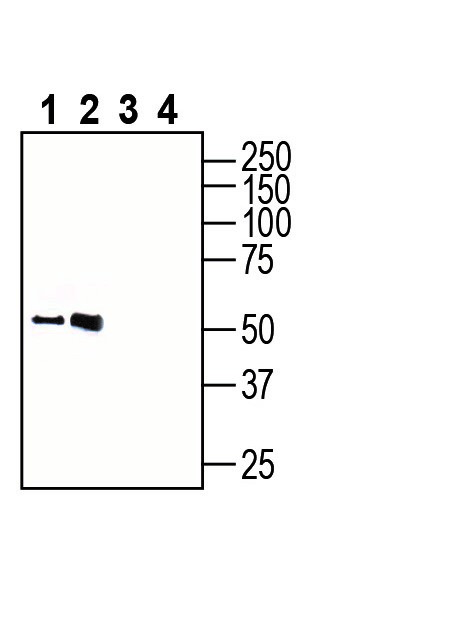 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR18 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-068), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR18 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-068), (1:200).
3-4. Anti-GPR18 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR18 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR068).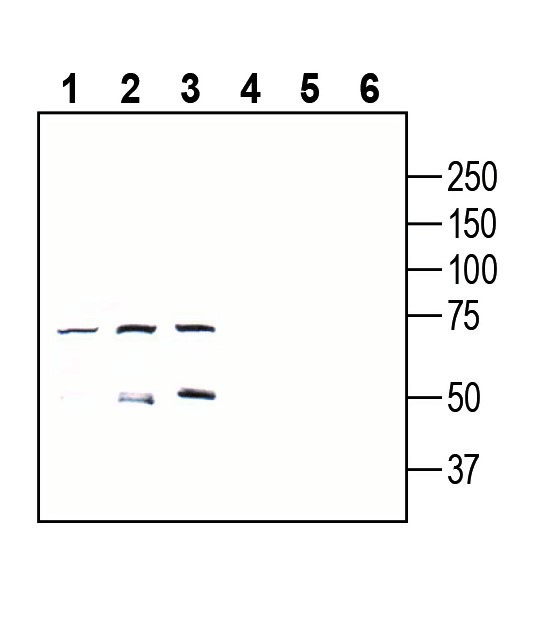 Western blot analysis of mouse EL4 T-cell lymphoma cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse WEHI-231 B-cell lymphoma cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and mouse BV-2 microglia cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-GPR18 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-068), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse EL4 T-cell lymphoma cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse WEHI-231 B-cell lymphoma cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and mouse BV-2 microglia cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-GPR18 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-068), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-GPR18 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR18 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR068).
G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) comprise a large superfamily of receptors characterized by a seven transmembrane domain structure and an ability to activate intracellular transducer G proteins. Over 800 GPCRs in five main families have been identified in eukaryotes on the basis of genomic sequence analysis 1-2. These receptors can be activated by hormones, neurotransmitters, odorants, light, or pheromones. GPCRs mediate the signaling of extracellular stimuli to intracellular responses via activation of heterotrimeric G proteins and their subsequent interaction with effector proteins. GPCRs have been implicated in a number of physiological functions including development of anxiety, behavior, homeostasis, cognition, appetite, and drug addiction 3. The GPCR family contains a diverse group of cell-surface mediators of signal transduction, its size exceeding other cell-surface protein receptors including the tyrosine kinase receptors, guanylyl cyclase receptors and ligand-gated ion channels 4.
The murine homolog of GPR18 was first isolated in 1996 5. A potential agonist for this orphan receptor was proposed only in 2006 when N-arachidonylglycine (NAGly) was shown to increase calcium concentration and inhibit forskolin induced cAMP production in CHO cells in a pertussis sensitive manner 6.
GPR18 shares low sequence homology with the cannabinoid receptors CB1R and CB2R (~13% and 8%) and moderate identity with the putative cannabinoid receptor GPR55 (21%). Nonetheless, it has been related to the endocannabinoid system since a range of endogenous, phytogenic and synthetic cannabinoids have shown to modulate GPR18 7.
GPR18 was shown to be constitutively active in melanomas, acting as an apoptosis inhibitor 8, while playing a reverse role in macrophage apoptosis, that is, signaling for cell death9. Both of these roles were mediated via Gαi pathways. Work on alternate cannabinoid compounds as potential agonist showed differential activation of Gαq / Gαi signaling suggesting biased agonism in pathway selection10.
