Overview
- Peptide (C)GND(S)DLYAHHSTAR, corresponding to amino acid residues 18 - 31 of human GPR183 (Accession P32249). Extracellular, N-terminus.

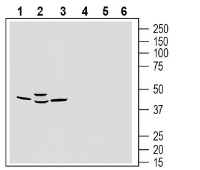 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain lysates (lanes 2 and 5) and rat lung membranes (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-GPR183 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-063), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain lysates (lanes 2 and 5) and rat lung membranes (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-GPR183 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-063), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-GPR183 Antibody, preincubated with GPR183 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR063). Western blot analysis of rat spleen membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse spleen membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR183 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-063), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat spleen membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse spleen membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR183 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-063), (1:200).
3-4. Anti-GPR183 Antibody, preincubated with GPR183 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR063). Western blot analysis of human Daudi B-lymphoblast cell line lysates (lanes 1 and 3) and human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysates (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR183 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-063), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human Daudi B-lymphoblast cell line lysates (lanes 1 and 3) and human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysates (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR183 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-063), (1:200).
3-4. Anti-GPR183 Antibody, preincubated with GPR183 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR063).
 Expression of GPR183 in in rat parietal cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-GPR183 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-063), (1:1200), followed by donkey anti-rabbit-biotin and streptavidin-Cy3. A. GPR183 immunoreactivity (red) appears in soma and apical dendrite profiles (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with GPR183 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR063), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of GPR183 in in rat parietal cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-GPR183 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-063), (1:1200), followed by donkey anti-rabbit-biotin and streptavidin-Cy3. A. GPR183 immunoreactivity (red) appears in soma and apical dendrite profiles (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with GPR183 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR063), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Kurschus FC, Wanke F. (2018), Biochimie., 153, 52.
- Daugvilaite et al (2014), Eur J Immunol., 44, 1904.
- Duc et al (2019), Int J Mol Sci., 20, 4522.
- Yi et al (2012), Immunity, 37, 535.
G-protein coupled receptor 183 (GPR183) also known as Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 2 (EBI2), is a chemotactic receptor that participates in the migratory capability of cells 2. It belongs to the rhodopsin-like subfamily of class A transmembrane spanning (7TM) G protein-coupled receptors and its most potent ligand is oxysterol 7α-25-OHC 1.
Dihydroxycholesterols, such as oxysterol 7α-25-OHC, are generated from cholesterol in steady state but also in the context of inflammation. GPR183 senses these oxysterols and induces chemotactic migration of immune cells towards higher concentrations of these ligands and hence cells that express GPR183 are trafficking through an oxysterol gradient dependent manner acting like chemokine processes. The migratory function of this receptor affects several important immune processes, in particular, GPR183 is involved in the T-dependent antibody response in the germinal centers. This puts GPR183 in a unique position to effect autoimmunity and inflammatory bowel diseases 3,4.
In addition, GPR183 is highly expressed by type 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3) and its oxysterol ligand was shown to be essential for the localization and the migration of ILC3s and to have a critical role for the formation of lymphoid tissues in the mouse colon during colitis 2.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-GPR183 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-063) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize GPR183 from mouse, rat and human samples.

