Overview
|
Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-051) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the mouse GPR35. The antibody can be used in western blot and live cell flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize GPR35 from mouse and rat samples. The antibody will not recognize the receptor from human samples.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Applications
 Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-051), (1:200). 3-4. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR35 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR051).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-051), (1:200). 3-4. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR35 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR051).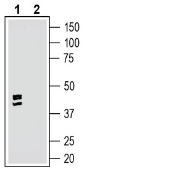 Western blot analysis of rat dorsal root ganglion lysate:1. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-051), (1:200). 2. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR35 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR051).
Western blot analysis of rat dorsal root ganglion lysate:1. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-051), (1:200). 2. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR35 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR051). Western blot analysis of rat small intestine lysate:1. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-051), (1:200). 2. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR35 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR051).
Western blot analysis of rat small intestine lysate:1. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-051), (1:200). 2. Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR35 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-GR051).
 Expression of GPR35 in rat dorsal root ganglion.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) sections with Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-051), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. GPR35 immunoreactivity (green) appeared in neuron profiles (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with GPR35 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GR051), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of GPR35 in rat dorsal root ganglion.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) sections with Anti-GPR35 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-051), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. GPR35 immunoreactivity (green) appeared in neuron profiles (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with GPR35 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GR051), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Specifications
- Peptide (C)EGGF(S)FSSQTRRNFS, corresponding to amino acid residues 156 - 170 of mouse GPR35 (Accession Q9ES90). Extracellular, 2nd loop.

Scientific Background
G- protein coupled receptor 35 (GPR35) is an "orphan" GPCR, whose native ligand is still unknown. It was shown to be involved in the modulation of synaptic transmission, nociception, neuropathic and inflammatory pain, and in various diseases including ulcerative colitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis1 and hence there is a great therapeutic potential in studying its activity.
In vitro, GPR35 is stimulated by high concentrations of a number of small molecules, including kynurenic acid, 2-oleoyllysophosphatidic acid, DHICA, reverse T3, cGMP and it has a wide range of synthetic agonists and antagonists that either activate or inactivate it, respectively (Summarized in2).
GPR35 is composed of seven trans-membrane domains, and it was shown to share structural homology with various receptors for chemokines; chemotactic cytokines that direct the traffic of leukocytes and other cells in the body. It was shown to be activated by chemokine CXCL17, and hence the role of a chemokine receptor was also assigned to it3.
GPR35 expression has been identified within discrete regions of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system, and lower levels in heart, lung and skeletal muscle, and also in the lower gut and colon and by various white cell groups, including numerous dendritic cell and monocyte populations4.
- Yang. et al. (2015), Inflamm. Bowel Dis., 21, 1.
- Mackenzie and Milligan. (2017), Neuropharmacology, 113, 661.
- Milligan. (2018), Br J Pharmacol., 175, 2543.
- Cosi. et al. (2011), Neuropharmacology, 60, 1227.

