Overview
- Peptide (C)KPKHDWTRTYFR, corresponding to amino acid residues 309-320 of mouse GPR39 (Accession Q5U431). 3rd extracellular loop.
- Mouse kidney and brain lysates. Rat colon and pancreas lysates. Human HT-29 colorectal adenocarcinoma and human MEG-01 megakaryoblastic leukemia cell lysates (1:200- 1:1000).
 Western blot analysis of mouse kidney (lanes 1 and 3) and brain (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2 Anti-GPR39 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-045), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse kidney (lanes 1 and 3) and brain (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2 Anti-GPR39 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-045), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-GPR39 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR39 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GR045).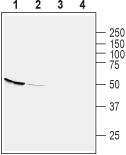 Western blot analysis of rat colon (lanes 1 and 3) and pancreas (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2 Anti-GPR39 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-045), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat colon (lanes 1 and 3) and pancreas (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2 Anti-GPR39 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-045), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-GPR39 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR39 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GR045). Western blot analysis of human HT-29 colorectal adenocarcinoma (lanes 1 and 3) and human MEG-01 megakaryoblastic leukemia (lanes 2 and 4) cell line lysates:1,2 Anti-GPR39 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-045), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human HT-29 colorectal adenocarcinoma (lanes 1 and 3) and human MEG-01 megakaryoblastic leukemia (lanes 2 and 4) cell line lysates:1,2 Anti-GPR39 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGR-045), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-GPR39 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GPR39 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GR045).
GPR39 (G-protein coupled receptor 39) is member of the rhodopsin-like family of 7-transmembrane containing GPCRs and is closely related to the ghrelin/neurotensin receptor subfamily.
The human GPR39 gene encodes the full-length receptor (GPR39-1a). GPR39 is expressed in various tissues including adipose tissue, heart and thyroid but is most abundant in the pancreas, GI tract, liver and kidney.
The GPR39 receptor is comprised of an extracellular N-terminus, seven membrane spanning loops, and an intracellular C-terminus. It also contains four cysteine residues in its extracellular domains. These have been shown to form two disulfide bridges which are conserved within all vertebrate GPR39 sequences with the exception that the first bridge is absent from the fish receptors.
Although GPR39 has a high degree of constitutive activity mediated through Gαq and Gα12/13 pathways, it has been discovered recently that Zn2+ serves as a ligand capable of activating the receptor. Following Zinc activation, both pathways are significantly enhanced and signaling occurs through the Gαs pathway as well.
GPR39 has been implicated in several pathologies: Disruption of the GPR39 gene is associated with impaired insulin secretion. GPR39 knockout mice exhibit decreased insulin levels and lower levels of insulin promoting factor-1 and HNF-1α in pancreatic islets. GPR39 knockout mice also exhibit lower levels of CREB and BDNF proteins that are important in neuronal plasticity and antidepressant response thus leading to depressive-like behaviors in animals.
