Overview
- Peptide (C)HRV(S)FEHYPIQAWQR, corresponding to amino acid residues 169-183 of mouse GPR68 (Accession Q8BFQ3). 2nd extracellular loop
 Cell surface detection of GPR68 by direct flow cytometry in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of GPR68 by direct flow cytometry in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + Rabbit IgG Isotype control-APC (#RIC-001-APC).
___ Cells + Anti-GPR68 (OGR1) (extracellular)-APC Antibody (#AGR-042-APC), (5 µg). Cell surface detection of GPR68 by direct flow cytometry in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of GPR68 by direct flow cytometry in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + Rabbit IgG Isotype control-APC (#RIC-001-APC).
___ Cells + Anti-GPR68 (OGR1) (extracellular)-APC Antibody (#AGR-042-APC), (5 µg).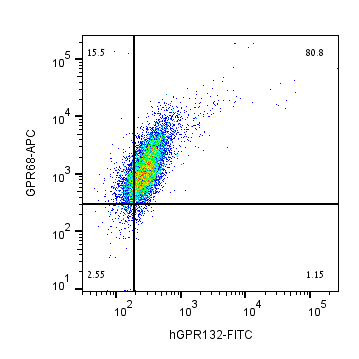 Multicolor flow cytometry with GPR68 and GPR132Human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line was labeled by adding Anti-GPR68 (OGR1) (extracellular)-APC Antibody (#AGR-042-APC), (5µg) and Anti-Human GPR132/G2A (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#AGR-046-F), (5µg).
Multicolor flow cytometry with GPR68 and GPR132Human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line was labeled by adding Anti-GPR68 (OGR1) (extracellular)-APC Antibody (#AGR-042-APC), (5µg) and Anti-Human GPR132/G2A (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#AGR-046-F), (5µg).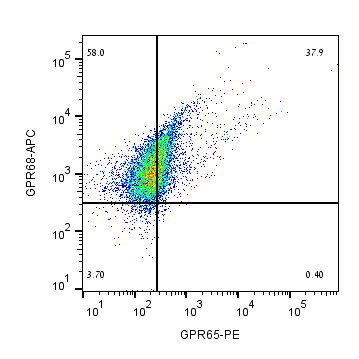 Multicolor flow cytometry with GPR68 and GPR65Human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line was labeled by adding Anti-GPR68 (OGR1) (extracellular)-APC Antibody (#AGR-042-APC), (5µg) and Anti-GPR65 (TDAG8) (extracellular)-PE Antibody (#AGR-043-PE), (5µg)
Multicolor flow cytometry with GPR68 and GPR65Human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line was labeled by adding Anti-GPR68 (OGR1) (extracellular)-APC Antibody (#AGR-042-APC), (5µg) and Anti-GPR65 (TDAG8) (extracellular)-PE Antibody (#AGR-043-PE), (5µg)
All GPCRs, including GPR68, are single peptides possessing seven transmembrane domains with an extracellular N-terminus and an intracellular C-terminus1. GPR68 is expressed in several tissues including the spleen, testis, small bowel, brain, heart, lung and kidneys. It shares strong homology (49-54%) with the human receptor GPR42.
GPR68 is proton sensitive in the pH range of 6.8-7.8 and acts as a proton activated receptor. GPR68 stimulates inositol triphosphate (IP3) formation thereby releasing intracellular calcium and activating the mitogen activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated (ERK) kinase cascade. In addition, GPR68 receptor regulates NHE3 and H+-ATPase, in response to extracellular pH changes in cultured HEK 293 renal cells. This activation requires a cluster of histidine residues in the extracellular domains of the receptor and protein-kinase C (PKC) activation4.
