Overview
- Peptide (C)RNVRIASRLDSWPQG, corresponding to amino acid residues 248-262 of rat GPR91 (Accession Q6IYF9). 3rd extracellular loop.
- Human THP-1 monocytic leukemia and Jurkat T-cell leukemia cells and mouse J774 macrophage cells (2.5 µg).
 Cell surface detection of GPR91 in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of GPR91 in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + rabbit IgG isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-GPR91 (SUCNR1) (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ASR-090-F), (2.5 µg).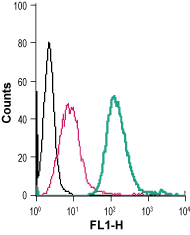 Cell surface detection of GPR91 in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of GPR91 in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + rabbit IgG isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-GPR91 (SUCNR1) (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ASR-090-F), (2.5 µg). Cell surface detection of GPR91 in live intact human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of GPR91 in live intact human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + rabbit IgG isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-GPR91 (SUCNR1) (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ASR-090-F), (2.5 µg).
GPR91 (Succinate Receptor 1), a member of the GPCR superfamily, is specifically activated by extracellular succinate outside the tricarboxylic acid cycle, resulting in activation of paracrine and endocrine effectors. Activation of GPR91 is associated with several diseases, including hypertension and diabetes1,2.
GPR91 was shown to regulate normal retinal vascularization, proliferative ischemic retinopathy and cortical revascularization post-ischemia. Activation of GPR91 influences different tissues such as kidney, heart, retina, white adipose tissue, and liver.
Through the activation of GPR91, succinate affects motility, migration, and growth of dendritic cells. In addition, the receptor directly promotes chemotaxis and potentiates activation initiated by Toll-like receptor agonists in dendritic cells1-3.
In the heart GPR91 mediates succinate-induced cardiomyocyte death. It was demonstrated that upholding levels of serum succinate can cause cardiac hypertrophy through the activation of the GPR911,2.
