Overview
- Peptide (C)EEAGPAGEPRGSQAS, corresponding to amino acid residues 147-161 of human HCN2 (Accession Q9UL51). Intracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat brain membranes (1:200-1:1000). Addition of 0.1-0.5 Tween-20 to the antibody solution is recommended.
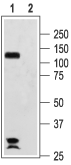 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-HCN2 Antibody (#APC-030), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-HCN2 Antibody (#APC-030), (1:200).
2. Anti-HCN2 Antibody, preincubated with HCN2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC030).
- Rat thalamus lysate (Whitacker, G.M. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 22900.).
- Rat brain membrane sections and mouse hypothalamus.
- Rat DRG primary culture (fixed and permeabilized) (1:100).
Hyperpolarization-activated cation currents (Ih) appear in the heart and the brain having crucial role in controlling electrical pacemaker activity, contributing to biological processes such as heartbeat, sleep-wake cycle and synaptic plasticity.1,2
The Ih currents are generated by the hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel family (HCN), which comprises four homologous members, named HCN1-4. Each HCN subunit consist of six transmembrane domains (TM), a pore region between TM5-TM6 and a binding domain to cyclic nucleotides (CNBD) in the cytoplasmic C-terminus.2
The HCN subunits can form functional homomers and can also co-assemble into functional heteromers.2
The channels are closely related to each other and share homology of about 60%. However, they are diverging from each other in their cytoplasmic N- and the C-terminus. The channels HCN1-4 mainly differ from each other with regard to their speed of activation and the extent by which they are modulated by cAMP. HCN1 is the fastest channel, followed by HCN2, HCN3 and HCN4.2,3
HCN2 is the most abundant neuronal channel and is found almost ubiquitously in the brain.3
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
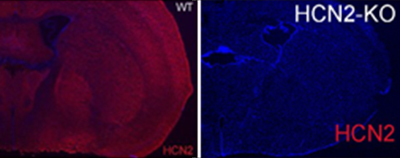
Knockout validation of Anti-HCN2 Antibody in mouse brain.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse coronal brain sections using Anti-HCN2 Antibody (#APC-030). HCN2 staining (red) is broadly detected across the coronal section. Lack of HCN2 staining is observed in HCN2-/- mice. Adapted from Hammelmann, V. et al. (2011) PLoS ONE 6, e17078.
