Overview
- Peptide (C)KKQPGQPRPTSK, corresponding to amino acid residues 203-214 of human Orai1 (Accession Q96D31). 2nd extracellular loop.

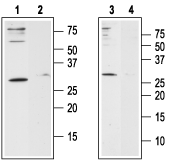 Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 2) and human HL-60 acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 4):1,3. Anti-Human Orai1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-060), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 2) and human HL-60 acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 4):1,3. Anti-Human Orai1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-060), (1:200).
2,4. Anti-Human Orai1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Human Orai1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC060).
 Cell surface detection of Orai1 by indirect flow cytometry in live intact human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of Orai1 by indirect flow cytometry in live intact human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + goat-anti-rabbit-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-Human Orai1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-060), (5μg) + goat-anti-rabbit-FITC.- The control antigen is not suitable for this application.
- Eisner, D.A. et al. (2005) Exp.Physiol. 90, 3.
- Chakrabarti, R. and Chakrabarti, R. (2006) J.Cell. Biochem. 99, 1503.
- Feske, S. et al. (2006) Nature 441, 179.
- Pickett, J. (2006) Nature Reviews Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 794.
- Luik, R.M. et al. (2006) J.Cell. Biol. 174, 815.
- Wu, M.M. et al. (2006) J.Cell. Biol. 174, 803.
- Hong H.L. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 9105.
- Luik, R.M and Lewis, R.S. (2007) Trends Mol. Med. 13, 103.
- DeHaven, W.I. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 17548.
Cytosolic calcium (Ca2+) has long been known to act as a key second messenger in many intracellular pathways including synaptic transmission, muscle contraction, hormonal secretion, cell growth and proliferation.1,2 The mechanism controlling intracellular Ca2+ level influx either by the calcium-release-activated Ca2+ channels (CRAC), or from intracellular stores, has become of great interest.
Recently, several key players of the store operated complex have been identified3. Orai1 (also known as CRACM1) acts as the store operated Ca2+ channel (SOC) and STIM1, which acts as the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ sensor3,4. The formation of functional channels requires the presence of both Orai1 and STIM1 proteins working as a complex and involves the co-clustering of Orai1 on the plasma membrane with STIM1 on the endoplasmic reticulum4-6. TRPC1, a member of the transient receptor potential family was also suggested to act as a player in the SOC complex7. In T-cells, Ca2+ entry following activation by antigen-receptor engagement occurs solely through CRAC channels where Orai1 constitutes the pore forming subunit3,8.
Orai1 is a plasma membrane protein with four potential transmembrane domains and intracellular N- and C-terminus. In addition, two mammalian homologs to Orai1 have been identified; Orai2 and Orai33,9. All three, Orai1 Orai2 and Orai3, are capable of forming store operated channels with different magnitudes9.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Human Orai1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-060) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, and indirect flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize Orai1 from human samples only.
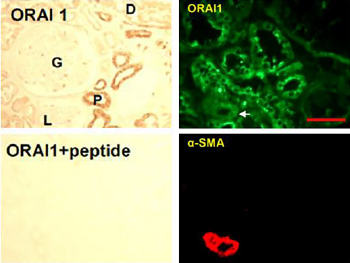
Expression of Orai1 in human kidney.Immunohistochemical staining of human kidney sections using Anti-Human Orai1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-060). In paraffin-embedded kidney sections, Orai1 is localized to kidney tubules, with stronger staining in the proximal tubules (upper left panel). Antibody preabsorbed with the control antigen (supplied with the antibody) was used as control to show the specificity of the antibody (lower left panel). In frozen kidney sections, Orai1 staining (green) is observed in renal tubules (upper right panel). Smooth muscle actin staining is shown in red (lower right panel).Adapted from Zeng, B. et al. (2017) Nat. Commun. 8, 1920. with permission of SPRINGER NATURE.
Applications
Citations
- Human kidney lysate.
Zeng, B. et al. (2017) Nat. Commun. 8, 1920. - Human HK2 kidney cell lysate.
Mai, X. et al. (2016) J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 27, 3063. - Human OUMS-27 chondrosarcoma cell lysate.
Inayama, M. et al. (2015) Cell Calcium 57, 337. - Human airway smooth muscle cell lysate (1:1000).
Sathish, V. et al. (2015) Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 36, 1101. - Human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) lysate.
Zhou, M.H. et al. (2014) J. Biol. Chem. 289, 29446. - Human primary coronary artery smooth cell lysate.
Munoz, E. et al. (2013) Cell Calcium 54, 375. - Human HL-60 promyelocytic cell lysate.
Brechard, S. et al. (2008) Cell Calcium 44, 492.
- Human kidney sections.
Zeng, B. et al. (2017) Nat. Commun. 8, 1920.
- Human DU-145 prostate cells (1:200).
Stagno, M.J. et al. (2017) Cell Physiol. Biochem. 42, 1366.
- Motiani, R.K. et al. (2013) FASEB J. 27, 63.
- Abcejo, A.J. et al. (2012) PLoS ONE 7, e44343.
- Mitchell, C.B. et al. (2012) J. Neurochem. 122, 1155.
- Park, K.H. et al. (2011) Science Signaling 4, ra31.
- Meuchel, L.W. et al. (2011) Am. J. Physiol. 301, L91.
- Li, J. et al. (2011) Br. J. Pharmacol. 164, 382.
- Steinckwich, N. et al. (2011) J. Immunol. 186, 2182.
- Lur, G. et al. (2011) Biochem. J. 436, 231.
- Schaff, U.Y. et al. (2010) Blood 115, 657.
- Bisaillon, J.M. et al. (2010) Am. J. Physiol. 298, C993.
- Bomben, V.C. and Sontheimer, H. (2010) Glia 58, 1145.
- Fernandez-Rodriguez, S. et al. (2009) Cardiovasc. Res. 84, 470.
- Bréchaud, S. et al. (2008) Cell Calcium 44, 492.
