Overview
- Peptide (C)RIGLLGHPPHMNVNPQQPA, corresponding to amino acid residues 2732-2750 of rat IP3R1 (Accession P29994). Intracellular, C-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-IP3 Receptor-1 (ITPR1) Antibody (#ACC-019), (1:2000).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-IP3 Receptor-1 (ITPR1) Antibody (#ACC-019), (1:2000).
2. Anti-IP3 Receptor-1 (ITPR1) Antibody, preincubated with IP3 Receptor-1/ITPR1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC019).
- Rat superior cervical ganglia (SGC) lysate (Zhang, H. et al. (2013) Neuroscience 254, 70.).
 Expression of IP3R1 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum with Anti-IP3 Receptor-1 (ITPR1) Antibody (#ACC-019). Immunoreactivity appears in Purkinje cells (arrows in A) and their dendritic trees. In addition, axonal processes coursing through cerebellar white matter are visualized (arrow in B).
Expression of IP3R1 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum with Anti-IP3 Receptor-1 (ITPR1) Antibody (#ACC-019). Immunoreactivity appears in Purkinje cells (arrows in A) and their dendritic trees. In addition, axonal processes coursing through cerebellar white matter are visualized (arrow in B).
- Blondel, O. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268, 11356.
- V'arnai, P. et al. (2005) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 7859.
- Cai, W. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 23691.
Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) serves as a second messenger for many neurotransmitters, hormones and growth factors.1 The binding of IP3 to its receptor (IP3R), which is a ligand-gated Ca2+ channel, located predominantly at the endoplasmic reticulum, results in a rapid release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores.1
To date, three known isoforms of IP3R are known (designated IP3R1, IP3R2, and IP3R3) that can work as homotetramers or hetrotetramers. All three receptors have six transmembrane domains and a pore region between TM5 and TM6. The N-terminus as well as the C-terminus face the cytoplasm. Each IP3R consists of an N-terminal ligand binding domain (LBD) and a C-terminal domain which is linked by a long regulatory domain. The C-terminus is constitutively active, suggesting that the regulatory domain is required in order to maintain the suppression of channel activity.2
IP3R1 is one of the most important channels responsible for Ca2+ release from intracellular stores and was shown to be the predominant isoform expressed in the central nervous system. IP3R1 is a pivotal player in many neuronal functions, amongst them, neuronal plasticity and neurite extension.3
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-IP3 Receptor-1 (ITPR1) Antibody (#ACC-019) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize IP3R1 from human, rat, and mouse samples.
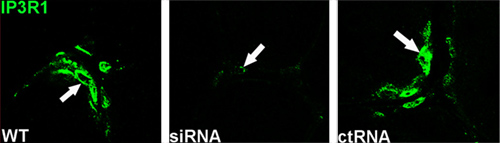
Expression of IP3 receptor 1 in TA muscle sections.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse muscle sections using Anti-IP3 Receptor-1 (ITPR1) Antibody (#ACC-019). IP3R1 staining (green) is detected at the neuromuscular junction (upper panel). Staining is almost completely eradicated upon siRNA treatment (middle panel). IP3R1 specific staining is shown upon scrambled RNA (ctRNA) treatment (lower panel).Adapted from Zhu, H. et al. (2011) J. Neurosci. 31, 15269. with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.
Applications
Citations
- Rat brain lysate (1:4000).
Kaya, L. et al. (2013) Biochim. Piophys. Acta 1833, 1421. - Mouse C2C12 myoblast cell lysate. Also tested in siRNA treated cells.
Zhu, H. et al. (2011) J. Neurosci. 31, 15269. - Rat brain and cerebral artery lysates (1:1000).
Zhao, G. et al. (2008) Am. J. Physiol. 295, C1376. - Rat A7r5 cell lysate. Also tested in siRNA treated cells.
Shirane, D. et al. (2004) Nat. Genet. 36, 190.
- Rat superior cervical ganglia (SGC) lysate.
Zhang, H. et al. (2013) Neuroscience 254, 70.
- Mouse tiabilis arterior muscle sections.
Zhu, H. et al. (2011) J. Neurosci. 31, 15269. - Rat brain sections.
Kaufmann, W.A. et al. (2009) J. Comp. Neurol. 515, 215. - Zebrafish brain sections (1:100).
Bai, Q. et al. (2007) Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 6501.
- Mouse C2C12 myoblast cells.
Zhu, H. et al. (2011) J. Neurosci. 31, 15269.
