Overview
- Peptide RQELRKLKRRFLEEHEC, corresponding to amino acid residues 53-69 of human KCNK1 (Accession O00180). Extracellular, near the P1 loop.
- Rat brain lysate (1:200) and HEK-KCNK1 transfected cells (1:300).
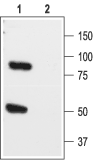 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate:1. Anti-KCNK1 (TWIK-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-110), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate:1. Anti-KCNK1 (TWIK-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-110), (1:200).
2. Anti-KCNK1 (TWIK-1) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with KCNK1/TWIK-1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC110). Western blot analysis of HEK-293-KCNK1 transfected cells:1. Anti-KCNK1 (TWIK-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-110), (1:300).
Western blot analysis of HEK-293-KCNK1 transfected cells:1. Anti-KCNK1 (TWIK-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-110), (1:300).
2. Anti-KCNK1 (TWIK-1) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with KCNK1/TWIK-1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC110).
- Rat brain sections.
KCNK1 (also named TWIK-1 or K2P1.1) is a member of the 2-pore (2P) domain K+ channels family that, currently, includes 16 members. These channels show little time- or voltage-dependence and are considered to be “leak” or “background” K+ channels, thereby generating background currents which help set the membrane resting potential and cell excitation. The K2P channels have a signature topology that includes four transmembrane domains and two pore domains with intracellular N- and C termini.
K2P channels are regulated by diverse physical and chemical stimuli including temperature, pH, mechanical stretch, inhalation anesthetics, etc. but are insensitive to the classical K+ channel blockers.
KCNK1 was the first of the K2P channels to be identified and as its original name indicates (Tandem of P domains in a Weak Inward rectifier K+ channel) the channel behaves as a weak inward rectifier when expressed in heterologous systems. The channel is ubiquitously expressed with the most prominent expression in the brain, kidney and heart.
