Overview
- Peptide TFRNYSLDEEKKEDETEKMC, corresponding to amino acid residues 475-494 of rat KCNK10 (Accession Q9JIS4). Intracellular, C-terminal domain.
- Rat cerebellum lysate (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of rat cerebellum lysate:1. Anti-KCNK10 (TREK-2) Antibody (#APC-055), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat cerebellum lysate:1. Anti-KCNK10 (TREK-2) Antibody (#APC-055), (1:200).
2. Anti-KCNK10 (TREK-2) Antibody, preincubated with KCNK10/TREK-2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC055).
- Rat brain sections.
- HEK-293 cells transfected with TREK-2 (1:500) (Acosta, C. et al. (2014) J. Neurosci. 34, 1494.).
KCNK10 (TREK-2, K2P10.1) is a member of the 2-pore (2P) domain K+ channels. These K+ channels are also known as background or “leak” channels and help to set the resting membrane potential.
K2P channels can be activated by a wide variety of stimuli including temperature, pH, mechanical stretch, inhalation anesthetics, etc. The channels can also be subclassified based on their specific activators.
KCNK10 can be integrated to a K2P subfamily which includes K2P2.1 (TREK1) and K2P4.1 (TRAAK) that are activated by intracellular unsaturated fatty acids such as arachidonic acid, low intracellular pH and mechanical stretch. KCNK10 mRNA expression has been detected in the brain (primarily in the cerebellum) and in peripheral tissues such as pancreas and kidney.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
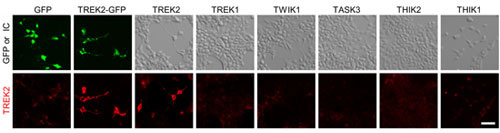 Expression of TREK-2 in HEK-293 transfected cellsImmunocytochemical staining of HEK-293 K2P transfected cells using Anti-KCNK10 (TREK-2) Antibody (#APC-055). TREK-2 staining is specific for HEK-293 cells transfected with TREK-2.Adapted from Acosta, C. et al. (2014) J. Neurosci. 34, 1494. with permission of The Society for Neuroscience.
Expression of TREK-2 in HEK-293 transfected cellsImmunocytochemical staining of HEK-293 K2P transfected cells using Anti-KCNK10 (TREK-2) Antibody (#APC-055). TREK-2 staining is specific for HEK-293 cells transfected with TREK-2.Adapted from Acosta, C. et al. (2014) J. Neurosci. 34, 1494. with permission of The Society for Neuroscience.
