Overview
- Peptide NLAFIDESSDTQSERGC, corresponding to amino acid residues 343-359 of human KCNK4 (Accession Q9NYG8). Intracellular, C-terminus.
- Rat cerebellum lysate (1:200) and HEK-293-KCNK4 transfected cells (1:200).
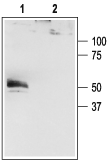 Western blot analysis of HEK-293-KCNK4 transfected cells:1. Anti-KCNK4 (TRAAK) Antibody (#APC-108), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of HEK-293-KCNK4 transfected cells:1. Anti-KCNK4 (TRAAK) Antibody (#APC-108), (1:200).
2. Anti-KCNK4 (TRAAK) Antibody, preincubated with KCNK4/TRAAK Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC108).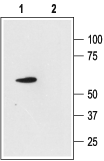 Western blot analysis of rat cerebellum lysate:1. Anti-KCNK4 (TRAAK) Antibody (#APC-108), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat cerebellum lysate:1. Anti-KCNK4 (TRAAK) Antibody (#APC-108), (1:200).
2. Anti-KCNK4 (TRAAK) Antibody, preincubated with KCNK4/TRAAK Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC108).
- Rat brain sections.
KCNK4 (also named TWIK-related arachidonic acid stimulated K+ channel, TRAAK or K2P4.1) is a member of the 2-pore (2P) domain K+ channels family that at the moment includes 16 members. These channels show little time- or voltage-dependence and are considered to be “leaky” or “background” K+ channels, thereby generating background currents which help set the membrane resting potential and cell excitation. The K2P channels have a signature topology that includes four transmembrane domains and two pore domains with intracellular N- and C- termini.
K2P channels are regulated by diverse physical and chemical stimuli including temperature, pH, mechanical stretch, inhalation anesthetics, etc. The channels can then be subclassified based in their specific activators. KCNK4 can be integrated to a K2P subfamily that includes K2P2.1 (TREK1) and K2P10.1 (TREK2) that are activated by intracellular unsaturated fatty acids such as arachidonic acid, lysophosphatidic acid, high intracellular pH and mechanical stretch.
KCNK4 expression is largely confined to the brain in mouse samples while in humans it is also expressed in placenta and to a lesser degree in kidney, small intestine and prostate.
