Overview
- Peptide (C)ESHQQLSASSHTDYASIPR, corresponding to residues 295-313 of human KCNK6 (Accession Q9Y257). Intracellular, C-terminus.
- Rat brain membranes (1:200).
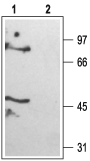 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-KCNK6 (TWIK-2) Antibody (#APC-040), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-KCNK6 (TWIK-2) Antibody (#APC-040), (1:200).
2. Anti-KCNK6 (TWIK-2) Antibody, preincubated with KCNK6/TWIK-2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC040).
KCNK6 (also named Tandem of P domain of Weak Inward rectifier K+ channel 2, TWIK-2 or K2P6.1) is a member of the 2-pore (2P) domain K+ channel family that includes at least 16 members. These channels show little time- or voltage-dependence and are considered to be “leak” or “background” K+ channels, thereby generating background currents which help set the membrane resting potential and cell excitation.
The K2P channels have a signature topology that includes four transmembrane domains and two pore domains with intracellular N- and C- termini. The functional channel is believed to be a dimer.
K2P channels are regulated by diverse physical and chemical stimuli including temperature, changes in intracellular pH, mechanical stretch, inhalation anesthetics, etc. The channels can then be subclassified based in their specific activators.
KCNK6 displays low single channel conductance of about 5pS and is partially activated by arachidonic acid and blocked by volatile anesthetics.
KCNK6 expression is widespread, especially in the rat were it is expressed in brain, heart, kidney and liver. In humans KCNK6 expression is more restricted with expression in aorta, stomach, placenta and spleen while in mouse, KCNK6 expression has been detected only in liver.
