Overview
- Peptide CSAMVEELRMSLK, corresponding to amino acid residues 858-870 of rat kainate receptor GluK2 (Accession P42260). Intracellular, C-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-GRIK2 (GluK2) Antibody (#AGC-009), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-GRIK2 (GluK2) Antibody (#AGC-009), (1:400).
3,4. Anti-GRIK2 (GluK2) Antibody, preincubated with GRIK2/GluK2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GC009).
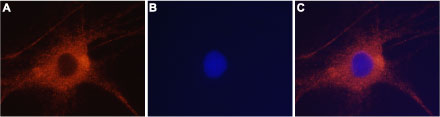 Expression of GluR6 in rat DRG neuronsImmunocytochemistry of rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. A. Paraformaldehyde-fixed and permeabilized DRG neurons were labeled with Anti-GRIK2 (GluK2) Antibody (#AGC-009), (1:400) followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-555 secondary antibody. B. Nuclei were visualized with the cell permeable dye Hoechst 33342 (blue). C. Merged figure of A and B.
Expression of GluR6 in rat DRG neuronsImmunocytochemistry of rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. A. Paraformaldehyde-fixed and permeabilized DRG neurons were labeled with Anti-GRIK2 (GluK2) Antibody (#AGC-009), (1:400) followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-555 secondary antibody. B. Nuclei were visualized with the cell permeable dye Hoechst 33342 (blue). C. Merged figure of A and B.
- Lerma, J. et al. (2001) Physiol. Rev. 81, 971.
- Dingledine, R. et al. (1999) Pharmacol. Rev. 51, 7.
L-Glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS), operates through several receptors that are categorized as ionotropic (ligand-gated cation channels) or metabotropic (G-protein-coupled receptors).
The ligand-gated ion channel family consists of fifteen members that have been subdivided into three families based upon their pharmacological profile: the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-preferring receptors, the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-preferring receptors, and the kainate-preferring receptors.
The kainate receptor subfamily consists of five members that have been further subdivided into two classes based upon structural homology and functional characteristics. GluR5, GluR6, and GluR7 receptor subunits share a high degree of homology and are able to form functional channels when expressed in heterologous systems. The KA-1 and KA-2 receptors are unable to form functional channels on their own, but when coexpressed with GluR5-7 receptor subunits, they form channels with high affinity for kainate.1,2
Like AMPA receptors, the functional unit of endogenous kainate receptors is believed to be a tetramer, which can be either homomeric or heteromeric. Kainate receptors GluR5 and GluR6 (but not GluR7, KA-1, or KA-2) can undergo RNA editing; as in the AMPA receptor GluR2, a glutamine (Q) residue in the channel pore is edited to encode arginine (R) in the mature protein. Substitution of Q with R modulates the properties of the channel, producing channels with reduced single channel conductance and lower permeability to Ca2+.1,2
GluR6 is expressed in the CNS in basal ganglia, cerebellum, and hipoccampus, as well as in the spinal cord. The exact physiological role of GluR6 is unclear, but a role in controlling neuronal excitability, synaptic integration, and synaptic plasticity has been proposed.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer Anti-GRIK2 (GluK2) Antibody (#AGC-009), a highly specific antibody directed against the intracellular C-terminus domain of the rat kainate receptor GluK2. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunofluorescence applications and will recognize GluR6 from rat, human and mouse origins.
Applications
Citations
- Marrocco, J. et al. (2012) J. Neurosci. 32, 17143.
