Overview
- Peptide (C)KNRINRAPERLGK, corresponding to amino acid residues 49-61 of rat kainate receptor GluK4 (Accession Q01812). Extracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat and mouse brain membranes (1:400-1:1200).
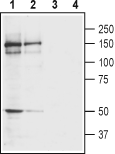 Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-GRIK4 (KA1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-041), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-GRIK4 (KA1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-041), (1:400).
3,4. Anti-GRIK4 (KA1) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with GRIK4/KA1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GC041).
- Rat immersion-fixed, free floating brain sections (1:100).
Glutamate is the principal excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS). Glutamate is involved in cognitive functions like learning and memory. Imbalances in glutamatergic transmission have profound physiological and behavioral consequences1.
Ionotropic glutamate receptors are classified functionally and by molecular homology into three receptor classes: N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA), and kainate (KA)2. KA receptors assemble as tetramers from five subunit types, GluK1, GluK2 GluK3, GluK4 and GluK5. The GluK1-GluK3 subunits have low glutamate affinity and are capable of forming functional homomeric channels. GluK4 and GluK5 are high-affinity kainate receptor subunits that bind glutamate but require coassembly with one or more GluK1-GluK3 subunits to form functional channels. The heteromultimeric assembly of kainate receptors like many other ion channels leads to the formation of receptors with unique pharmacological and functional properties3. Unlike the other KA receptor subunits, which are expressed throughout the CNS, GluK4 expression is limited to only a few regions of the brain, and expression is highest in the CA3 region of the hippocampus and dentate gyrus4.
The GluK4 receptor subunit gene, GRIK4, is located near the tip of the long arm of chromosome 11. Genetic variants in the GRIK4 gene have been demonstrated to associate with several psychiatric disorders. GRIK4 has been identified as a susceptibility gene in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder5. GluK4 may also play a role in excitotoxic neurodegeneration6.
