Overview
- GST fusion protein with the sequence SHSSHSSQSSSKKSSSVHSIPSTANRPNRPKSRESRDKQNATRMTRMGQAEKKWFTDEPDNAYPRNIQIKPMSTHMANQINQYKSTSSLIPPIREVEDEC, corresponding to residues 1097-1196 of mouse KCNMA1 variant 2 (Accession Q08460-2). Intracellular, C-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat bladder lysate:1. Guinea pig Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097–1096) Antibody (#APC-021-GP), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat bladder lysate:1. Guinea pig Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097–1096) Antibody (#APC-021-GP), (1:200).
2. Guinea pig Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097–1096) Antibody, preincubated with KCNMA1/KCa1.1 (1097-1196) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC021). Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Guinea pig Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097–1096) Antibody (#APC-021-GP), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Guinea pig Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097–1096) Antibody (#APC-021-GP), (1:200).
2. Guinea pig Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097–1096) Antibody, preincubated with KCNMA1/KCa1.1 (1097-1196) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC021).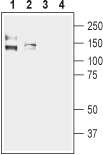 Western blot analysis of human Colo205 colon adenocarcinoma (lanes 1 and 3) and human Caco-2 colon adenocarcinoma cell lysates (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Guinea pig Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097–1096) Antibody (#APC-021-GP), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human Colo205 colon adenocarcinoma (lanes 1 and 3) and human Caco-2 colon adenocarcinoma cell lysates (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Guinea pig Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097–1096) Antibody (#APC-021-GP), (1:200).
3,4. Guinea pig Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097–1096) Antibody, preincubated with KCNMA1/KCa1.1 (1097-1196) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC021).
- Yuan, P. et al. (2010) Science. 329, 182.
- Cheng, Y.Y. et al. (2016) Mol. Cancer 15, 44.
- Petho, Z. et al. (2016) Arthritis Res. Ther. 18, 103.
High conductance voltage and Ca2+-activated K+ channels (also known as BK or Slo1 channels) are a family of K+ channels involved in various physiological processes including neuronal excitability and smooth muscle contraction.
KCa1.1 channel, also known as KCNMA1, is a member of the BK family and like other BK channels it is comprised of four identical subunits. Each unit consists of seven transmembrane segments and a large intracellular C-terminus. Transmembrane segments S1 to S4 form the channel’s voltage sensor; S5, S6 and the intervening amino acids form the pore and selectivity filter. The C-terminus forms a large cytoplasmic domain. This large domain accounts for two-thirds of the entire channel and is believed to contain the domain for Ca2+ binding. Two tandem C-terminal regulator of K+ conductance (RCK) domains from each of four channel subunits form a gating ring at the intracellular membrane surface. A sequence of amino acids that is known as the Ca2+ bowl, and is located within the second of the tandem RCK domains, creates four Ca2+ binding sites on the outer perimeter of the gating ring between RCK domains.
KCa1.1 is regulated, both by membrane depolarization and increased intracellular Ca2+ levels which cause the channel to open. This causes subsequent membrane hyperpolarization that closes voltage- and Ca2+-gated channels thus making KCa1.1 a negative feedback regulator for electrical excitation1.
KCa1.1 is implicated in the pathogenesis of several diseases. Elevated levels of KCa1.1 mRNA are detected in malignant pleural mesothelioma patients compared with control patients2. Also, blocking KCa1.1 reduces the symptoms of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis animal models.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the mouse KCNMA1 channel. Guinea pig Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097-1196) Antibody (#APC-021-GP, formerly AGP-014), raised in guinea pigs, can be used in western blot, immunoprecipitation, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize KCNMA1 from human, mouse and rat samples. The antigen used to immunize guinea pigs is the same as Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097-1196) Antibody (#APC-021) raised in rabbit. Our line of guinea pig antibodies enables more flexibility with our products such as multiplex staining studies, immunoprecipitation, etc.
