Overview
- GST fusion protein with the sequence
SHSSHSSQSSSKKSSSVHSIPSTANRPNRPKSRESRDKQNATRMTRMGQAEKKWFTDEPDNAYPRNIQIKPMSTHMANQINQYKSTSSLIPPIREVEDEC, corresponding to residues 1097-1196 of mouse KCNMA1 variant 2 (Accession Q08460-2). Intracellular, C-terminus. 
- Rat brain lysates (2 μg) (Park, S.M. et al. (2004) FEBS Lett. 570, 143.).
- Rat brain sections.
Mouse vomeronasal sections (Zhang, P. et al. (2008) J. Neurophysiol. 100, 1824.).
- Mouse vomeronasal neurons (Zhang, P. et al. (2008) J. Neurophysiol. 100, 1824.).
- Wallner, M. et al. (1999) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 4137.
- Xia, X.M. et al. (1999) J. Neurosci. 19, 5255.
- Orio, P. et al. (2002) News Physiol. Sci. 17, 156.
The KCa1.1 channel (also known as KCNMA1, BKCa, Maxi K+ or slo) is part of a structurally diverse group of K+ channels that are activated by an increase in intracellular Ca2+. KCa1.1 shows a large single channel conductance when recorded electrophysiologically and hence its name. It differs from the rest of the subfamily members in that it can be activated by both an increase in intracellular Ca2+ and by membrane depolarization. In addition, the KCa1.1 channel structurally differs from the other Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. While the latter group has a topology that resembles that of the voltage-dependent K+ channels, the KCa1.1 channel has an extracellular N-terminus domain as well as an additional transmembrane domain.
KCa1.1 is expressed in virtually all cell types where it causes hyperpolarization and helps to connect intracellular Ca2+ signaling pathways and membrane excitability.
Indeed, KCa1.1 channels play a crucial role in smooth muscle contractility, neuronal spike shaping and neurotransmitter release.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097-1196) Antibody (#APC-021) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunoprecipitation, immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize KCNMA1 from human, mouse, and rat samples.
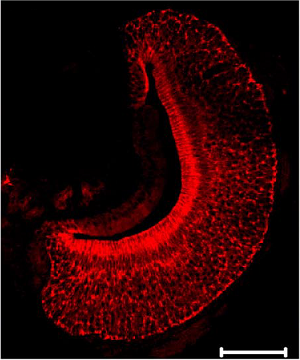 Expression of KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) in mouse VNO sections.Immunohistochemical staining of rat vomeronasal organ (VNO) sections using Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097-1196) Antibody (#APC-021). KCNMA1 staining (red) is specifically localized to the sensory epithelium with heavy labeling at the apical surface. Adapted from Zhang, P. et al. (2008) J. Neurophysiol. 100, 1824. with permission of The American Physiological Society.
Expression of KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) in mouse VNO sections.Immunohistochemical staining of rat vomeronasal organ (VNO) sections using Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097-1196) Antibody (#APC-021). KCNMA1 staining (red) is specifically localized to the sensory epithelium with heavy labeling at the apical surface. Adapted from Zhang, P. et al. (2008) J. Neurophysiol. 100, 1824. with permission of The American Physiological Society.Applications
Citations
 Expression of KCa1.1 in mouse SAN cells.Immunocytochemical staining of mouse sinoatrial cells (SANCs) using Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097-1196) Antibody (#APC-021). BK channel expression (red) overlaps with that of HCN4 (green). No detection of KCa1.1 was observed with the secondary antibody.
Expression of KCa1.1 in mouse SAN cells.Immunocytochemical staining of mouse sinoatrial cells (SANCs) using Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (1097-1196) Antibody (#APC-021). BK channel expression (red) overlaps with that of HCN4 (green). No detection of KCa1.1 was observed with the secondary antibody.
Adapted from Lai, M.H. et al. (2014) with permission of the American Physiological Society.
- Immunostaining of isolated mitochondria from mouse cardiomyocytes. Tested in KCNMA1-/- mice.
Goswami, S.K. et al. (2019) Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 5, 194.
- Mouse CCDcl1 cell lysate (1:1000).
Li, Y. et al. (2016) PLoS ONE 11, e0155006. - Rat brain and colon mucosal scraping lysates.
Perry, M.D. et al. (2016) Am. J. Physiol. 311, G785. - Mouse bladder lysate (1:1000). Also tested in KCa1.1 knockout mice.
Zemen, B.G. et al. (2015) Physiol. Rep. 3, e12612. - Mouse aorta lysate (1∶1000).
Rueda, A. et al. (2013) PLoS ONE 8, e53321. - Rat mesenteric arteries (1:300).
Shi, L. et al. (2013) Mech. Ageing Dev. 134, 416. - Rat cerebral arteries lysate.
Xie, M-J. et al. (2010) Am. J. Physiol. 298, C1489. - Rat heart endothelial cell lysate.
Ying, W-Z. et al. (2009) Hypertension 54, 1159. - HEK293T transfected cell lysates.
Alioua, A. et al. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283, 4808. - Mouse cerebral arteries (1:500).
Adebiyi, A. et al. (2007) Am. J. Physiol. 292, H1584. - Mouse cardiac tissues (1:300).
Ambroisine, M-L. et al. (2007) Circulation. 116, 2435. - Rat mesenteric arteries.
Bolognesi, M. et al. (2007) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 321, 187. - Mouse pulmonary artery.
Marino, M. et al. (2007) Am. J. Physiol. 293, L1171. - Rat renal arteries.
Michel, F.S. et al. (2007) Am. J. Physiol. 293, H1673. - Mouse kidney (1:100).
Yang, S-S. et al. (2007) Cell Metabol. 5, 331. - Mouse colons.
Hagen, B.M. and Sanders, K.M. (2006) Am J. Physiol. 291, C750. - Rat aortas.
Kiyoshi, H. et al. (2006) Am. J. Physiol. 291, H2723. - Mouse forebrain.
Moriguchi, S. et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 10811. - Rat superior mesenteric artery.
Bratz, I.N. et al. (2005) Am. J. Physiol. 289, H1277. - Feline circular smooth muscle esophagus (1:200).
Muinuddin, A. et al. (2005) Am. J. Physiol. 288, G1233. - Rat aorta and mesenteric artery (1:500).
Xu, H. et al. (2005) Hypertension 46, 1154. - Rat and pig brain.
Xi, Q. et al. (2004) Am J. Physiol. 286, H610. - Human left internal mammary arteries (LIMAs) and saphenous veins (SVs).
Archer, S.L. et al. (2003) Circulation 107, 769. - Rat basilar artery.
Gerzanich, V. et al. (2003) Circ. Res. 93, 805. - Guinea-pig ventricular myocytes.
Xu, W. et al. (2002) Science 298, 1029. - Rabbit ductus arteriosus.
Thebaud, B. et al. (2002) Pediatr. Res. 52, 19. - Rat pulmonary artery lysate.
Reeve, H.L. et al. (2001) J. Appl. Physiol. 90, 2249. - Ovine pulmonary artery.
Rhodes, M.T. et al. (2001) Am. J. Physiol. 280, L1250. - Mouse uterus smooth muscle lysate.
Benkusky, N.A. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 27712.
- Rat brain lysates (2 μg).
Park, S.M. et al. (2004) FEBS Lett. 570, 143.
- Rat colon sections (1:50).
Perry, M.D. et al. (2016) Am. J. Physiol. 311, G785. - Mouse cochlear duct (1:500).
Maison, S.F. et al. (2013) J. Neurophysiol. 109, 1525. - Mouse brain sections (1:750).
Montgomery, J.R. et al. (2013) Am. J. Physiol. 304, C299. - Rat mesenteric arteries (1:200).
Shi, L. et al. (2013) Exp. Physiol. 98, 326. - Rat artery sections (1:50).
Ellis, A. et al. (2009) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 330, 413. - Mouse organ of Corti inner hair cells.
Winter, H. et al. (2009) J. Neurosci. 29, 2581. - Rat heart sections.
Ying, W-Z. et al. (2009) Hypertension 54, 1159. - Mouse vomeronasal sections.
Zhang, P. et al. (2008) J. Neurophysiol. 100, 1824. - Mouse colonic tissue.
Flores, C.A. et al. (2007) J. Physiol. 583.2, 705. - Mouse cochleae (1:100).
Guipponi, M. et al. (2007) Am. J. Pathol. 171, 608. - Human mucosal biopsies from the ascending and sigmoid colon.
Sandle, G.I. et al. (2007) J. Pathol. 212, 66. - Mouse urinary bladder smooth muscle (UBSM) (1:1000).
Werner. M.E. et al. (2007) Am. J. Physiol. 292, R616. - Mouse brain (1:500).
Meredith, A.L. et al. (2006) Nat. Neurosci. 9, 1041. - Ovine pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMC).
Resnik, E. et al. (2006) Am. J. Physiol. 290, L761. - Rat brain sections (1:200).
Benhassine, N. and Berger, T. (2005) Eur. J. of Neurosci. 21, 914. - Mouse penis (1:1000).
Werner, M.E. et al. (2005) J. Physiol. 567.2, 545. - Rat Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) from mesenteric artery (MA) (1:400).
Xu, H. et al. (2005) Hypertension 46, 1154. - Mouse cochleae.
Ruttiger, L. et al. (2004) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 12922. - Human Odontoblasts.
Allard, B. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 25556.
- Isolated mitochondria from mouse cardiomyocytes. Also tested in KCNMA1-/- mice.
Goswami, S.K. et al. (2019) Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 5, 194. - Mouse BV-2 and primary microglia.
Yang, X. et al. (2019) J. Biol. Chem. 294, 12921. - Mouse CCDcl1 cells (1:100).
Li, Y. et al. (2016) PLoS ONE 11, e0155006. - HEK 293 transfected cells (1:500).
Velazquez-Merrero, C. et al. (2016) J. Neurosci. 36, 10625. - Mouse isolated SAN cells.
Lai, M.H. et al. (2014) Am. J. Physiol. 307, H1327. - Rat cerebral vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs).
Xie, M-J. et al. (2010) Am. J. Physiol. 298, C1489. - Rat T9 glioma cells.
Hoa, N. et al. (2009) PLoS One 4, e4631 - Mouse vomeronasal neurons.
Zhang, P. et al. (2008) J. Neurophysiol. 100, 1824. - Rat hippocampal neurons (1:250).
O’Malley, D. et al. (2005) FASEB J. 19, 1917. - Guinea-pigs vas deferens and urinary bladder smooth muscle cells.
Ohi, Y. et al. (2001) J. Physiol. 534.2, 313.
- Mouse BV-2 and primary microglia.
Yang, X. et al. (2019) J. Biol. Chem. 294, 12921.
- Yamashita, M. et al. (2006) FEBS J. 273, 3585.
- Pyott, S.J. et al. (2004) J. Neurosci. 24, 9469.
- Skinner, L.J. et al. (2003) J. Neurophysiol. 90, 320.
- Adamson, C.L. et al (2002) J. Neurosci. 22, 1385.

