Overview
- Peptide (C)DSSNPIES(S)QNFYKD, corresponding to amino acid residues 199-213 of rat KCNMA1 (Accession Q62976). 1st extracellular loop.
- Rat and mouse brain membranes (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-151), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-151), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with KCNMA1/KCa1.1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC151).
- Ovine arteriole sections (Tao, X. et al. (2015) Am. J. Physiol. 308, H707.).
- 5 µg antibody/1x106 human THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia cells.
- The blocking peptide is not suitable for this application.
The KCa1.1 channel (also known as KCNMA1, BKCa, Maxi K+ or slo) is part of a structurally diverse group of K+ channels that are activated by an increase in intracellular Ca2+. KCa1.1 shows a large single channel conductance when recorded electrophysiologically and hence its name. It differs from the rest of the subfamily members in that it can be activated by both an increase in intracellular Ca2+ and by membrane depolarization. In addition, the KCa1.1 channel structurally differs from the other Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. While the latter group has a topology that resembles that of the voltage-dependent K+ channels, the KCa1.1 channel has an extracellular N-terminus domain as well as an additional transmembrane domain.
KCa1.1 is expressed in virtually all cell types where it causes hyperpolarization and helps to connect intracellular Ca2+ signaling pathways and membrane excitability.
Indeed, KCa1.1 channels play a crucial role in smooth muscle contractility, neuronal spike shaping and neurotransmitter release.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
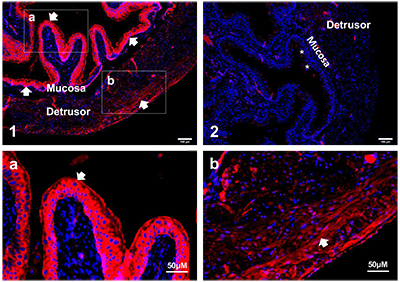
Expression of BKCa (KCNMA1) channel in mouse bladder.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse bladder sections using Anti-KCNMA1 (KCa1.1) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-151). BK staining (red) is detected in urothelium layer (panels 1, a) and in detrusor layer (panels 1, b). Negative control using secondary antibody only shows insignificant background staining (panel 2). DAPI is used to stain nuclei. Panels a, and b are high magnifications of panel 1.Adapted from Lu, M. et al. (2018) Am. J. Physiol. 314, C643. with permission of the American Physiological Society.
