Overview
- Synthetic peptide mapping to the 3rd extracellular loop of human KCNN4 (Accession O15554).
- HEK-KCa3.1 transfected cells, mouse MS1 endothelial cells, rat IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cells, human LN-CaP prostate carcinoma cells and human THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia cells (1:250).
 Western blot analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-051), (1:250):1. HEK cells transfected with control vector.
Western blot analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-051), (1:250):1. HEK cells transfected with control vector.
2. HEK cells transfected with human KCa3.1. Western blot analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-051), (1:250):1. Mouse MS1 endothelial cells.
Western blot analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-051), (1:250):1. Mouse MS1 endothelial cells.
2. Rat IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cells.
3. Human LN-CaP prostate carcinoma cells.
4. Human THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia cells.
- Mouse brain sections (Turner, K.L. and Sontheimer, H. (2014) Cereb. Cortex. 24, 2388.
- Live intact Raji (human Burkitt's lymphoma B cells) cell line and THP-1 (human acute monocytic leukemia cells) cell line.
- Live intact human LN-CaP prostate carcinoma cells (1:20).
KCa3.1 (KCNN4, SK4) is a member of the Ca2+ activated K+ channel family that shares the characteristic of being activated by intracellular Ca2+. The channel has an intermediate conductance, is voltage insensitive and is activated by Ca2+ in the submicromolar range. The channel has a similar topology to that of KV channels, that is, six transmembrane domains and intracellular N- and C-termini.
KCa3.1 is widely expressed in epithelial, endothelial and cells of hematopoietic origin. In erythrocytes (red blood cells) it has been identified as the molecular correlate of the so-called Gardos channel.
The functional role of the channel is to set the cell membrane potential at negative values so as to aid in the electrochemical transport of other ions such as Cl- and Ca2+. Indeed, KCa3.1 has a key role in sustaining the Ca2+ influx in activated T lymphocytes and in regulating Cl- secretion from colon epithelium. Therefore, specific blockers of the KCa3.1 channel have been proposed for the treatment of several diseases including autoimmune diseases, secretory diarrhea and sickle cell anemia.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
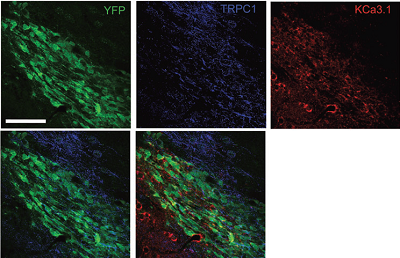 Multiplex staining of KCa3.1 (SK4) and TRPC1 in mouse brainImmunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-051) and Anti-TRPC1 Antibody (#ACC-010). YFP denotes neuroblasts. TRPC1 staining (blue) is detected in neuroblasts and outside neuroblasts as well (in astrocytes). KCa3.1 (red) is detected in neuroblasts. Merged image of all three staining (lower right panel) demonstrates the partial co-localization between the three.Adapted from Turner, K.L. and Sontheimer, H. (2013) Cereb. Cortex 24, 2388. with permission of Oxford University Press.
Multiplex staining of KCa3.1 (SK4) and TRPC1 in mouse brainImmunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-051) and Anti-TRPC1 Antibody (#ACC-010). YFP denotes neuroblasts. TRPC1 staining (blue) is detected in neuroblasts and outside neuroblasts as well (in astrocytes). KCa3.1 (red) is detected in neuroblasts. Merged image of all three staining (lower right panel) demonstrates the partial co-localization between the three.Adapted from Turner, K.L. and Sontheimer, H. (2013) Cereb. Cortex 24, 2388. with permission of Oxford University Press.
