Overview
- Peptide (C)NGVPESTSTDTPPDIDLHN, corresponding to amino acid residues 392-410 of human Kir2.1 (Accession P48049). Intracellular, C-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of mouse heart lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Guinea pig Anti-Kir2.1/KCNJ2 Antibody (#APC-026-GP), (1:500).
Western blot analysis of mouse heart lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Guinea pig Anti-Kir2.1/KCNJ2 Antibody (#APC-026-GP), (1:500).
3-4. Guinea pig Anti-Kir2.1/KCNJ2 Antibody, preincubated with Kir2.1/KCNJ2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC026).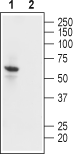 Western blot analysis of human U-87 MG glioblastoma cell lysate:1. Guinea pig Anti-Kir2.1/KCNJ2 Antibody (#APC-026-GP), (1:500).
Western blot analysis of human U-87 MG glioblastoma cell lysate:1. Guinea pig Anti-Kir2.1/KCNJ2 Antibody (#APC-026-GP), (1:500).
2. Guinea pig Anti-Kir2.1/KCNJ2 Antibody, preincubated with Kir2.1/KCNJ2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC026).
- Kubo, Y. et al. (1993) Nature 362, 127.
- Nichols, C.G. et al. (1996) Circ. Res. 78, 1.
- Plaster, N.M. et al. (2001) Cell 105, 511.
Kir2.1 is a member of the family of inward rectifying K+ channels. The family includes 15 members that are structurally and functionally different from the voltage-dependent K+ channels.1
The family’s topology consists of two transmembrane domains that flank a single and highly conserved pore region with intracellular N- and C-termini. As is the case for the voltage-dependent K+ channels the functional unit for the Kir channels is composed of four subunits that can assemble as either homo- or heterotetramers.
Kir channels are characterized by a K+ efflux that is limited by depolarizing membrane potentials thus making them essential for controlling resting membrane potential and K+ homeostasis.
Kir2.1 is a member of the Kir2.x subfamily that includes four members (Kir2.1- Kir2.4) that are characterized by strong inward rectification and high constitutive activity.
Kir2.1 is expressed in a variety of tissues including the heart, brain, vascular smooth muscle cells and skeletal muscles.
In the heart, Kir2.1 is a molecular component of the IK1 current that is responsible for setting the resting membrane potential, preventing membrane hyperpolarization due to Na+ pump activity, influencing propagation velocity, altering the electrical space constant, and promoting late phase repolarization.2 In fact, mutations in Kir2.1 channels have been linked to a form of long QT syndrome (LQT7) known as Andersen's syndrome that is characterized by cardiac arrhythmias, periodic paralysis, and dysmorphic features.3
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human Kir2.1 channel. Guinea pig Anti-Kir2.1/KCNJ2 Antibody (#APC-026-GP, formerly AGP-044) raised in guinea pig can be used in western blot analysis. It was designed to recognize Kir2.1 from human, rat and mouse samples. The antigen used to immunize guinea pigs is the same as Anti-Kir2.1/KCNJ2 Antibody (#APC-026) raised in rabbit. Our line of guinea pig antibodies enables more flexibility with our products such as multiplex staining studies, immunoprecipitation, etc.
