Overview
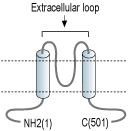
- Synthetic peptide mapping to the extracellular loop of human GIRK1 (Accession P48549).
 Expression of Kir3.1 in live intact human MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cell lineCell surface detection of Kir3.1 in live intact human MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. A. Cells were stained with Mouse Anti-GIRK1 (Kir3.1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-031), (1:20), followed by goat anti-mouse-DyLight-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Live view of the cells. C. Merge of the two images.
Expression of Kir3.1 in live intact human MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cell lineCell surface detection of Kir3.1 in live intact human MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. A. Cells were stained with Mouse Anti-GIRK1 (Kir3.1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-031), (1:20), followed by goat anti-mouse-DyLight-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Live view of the cells. C. Merge of the two images.
- Dascal, N. (1997) Cell Signal 9, 551.
- Wickman, K. et al. (1998) Neuron 20, 103.
- Mark, M.D. et al. (2000) Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 5830.
- Jin, W. and Lu, Z. (1998) Biochemistry 37, 13291.
- Kubo, Y. et al. (2005) Pharmacol. Rev. 57, 509.
Kir3.1 (or G-protein regulated inward-rectifier K+ channel 1, GIRK1) is a member of the family of inward rectifying K+ channels. The family includes 15 members that are structurally and functionally different from the voltage-dependent K+ channels.
The family’s topology consists of two transmembrane domains that flank a single and highly conserved pore region with intracellular N- and C-termini. As is the case for the voltage-dependent K+ channels, the functional unit for the Kir channels is composed of four subunits that can assemble as either homo- or heterotetramers.
Kir channels are characterized by a K+ efflux that is limited by depolarizing membrane potentials thus making them essential for controlling resting membrane potential and K+ homeostasis.
Kir3.1 is a member of the Kir3.x subfamily that includes four members (Kir3.1- Kir3.4). The Kir3 family is characterized by the fact that the channels can be activated by neurotransmitters and other factors acting via the activation of G-protein coupled receptors. Binding of the corresponding ligand to the G-protein receptor induces the dissociation of Gα-GTP from the Gβγ dimer. The latter directly binds to Kir3 and activates the channel1,3.
In the heart, Kir3.1 co-assembles with Kir3.4 to form the prototypical muscarinic-gated K+ channel KAch current, responsible for slowing the heart rate in response of parasympathetic stimulation2.
In the brain, Kir3.1 co-assembles with Kir3.2 and mediates the inhibitory effects of many neurotransmitters including opioid, adrenergic, muscarinic, dopaminergic and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)1,3.
A peptide toxin originating from the Apis mellifera bee venom, Tertiapin (#STT-250) was shown to be a potent blocker of Kir3.1 containing channels (8.6 nM for the Kir3.1/3.4 combination and 5.4 nM for the Kir3.1/3.2)4,5.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
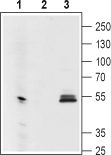
Mouse Anti-GIRK1 (Kir3.1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-031) is a highly specific mouse monoclonal antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize Kir3.1 from human, rat and mouse samples.