Overview
- Peptide RNAMNQDMEIGVT(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 6-18 of rat Kir3.4 (Accession P48548). Intracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat heart membranes (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-KCNJ5 (Kir3.4) Antibody (#APC-027), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-KCNJ5 (Kir3.4) Antibody (#APC-027), (1:200).
2. Anti-KCNJ5 (Kir3.4) Antibody, preincubated with KCNJ5/Kir3.4 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC027).
- Rat heart sections (1:20) (Atkinson, A.J. et al. (2013) J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2, e000246.).
- Mouse HL-1 cells (1:500) (Nobles, M. et al. (2010) Pflugers Arch. 460, 99.).
Kir3.4 is a member of the G-protein regulated inward-rectifier K+ (GIRK) channel subfamily which is part of an inward-rectifier K+ channel superfamily. The GIRK subfamily comprises four members in mammals (Kir3.1- Kir3.4) that present the common topology of the inward-rectifier superfamily: two transmembrane domains flanking a highly conserved pore region with the N and C-terminus located intracellularly.
Kir3.4 and the other Kir3 family subunits can be activated by neurotransmitters and other factors via the activation of G-protein coupled receptors. Binding of the corresponding ligand to the G-protein receptor induces the dissociation of G α-GTP from the Gβγ dimer. The latter directly binds to Kir3 and activates the channel.
Kir3.4 expression is largely confined to the heart, where it co-assembles with Kir3.1 to form the prototypical muscarinic-gated K+ channel KACh. Indeed, knockout mice for Kir3.4 showed impaired heart rate following vagal nerve stimulation.
A peptide toxin originating from the Apis mellifera bee venom, Tertiapin (#STT-250) was shown to be a potent blocker of Kir3.4 containing channels (8.6 nM for the Kir3.1/3.4 combination).4
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
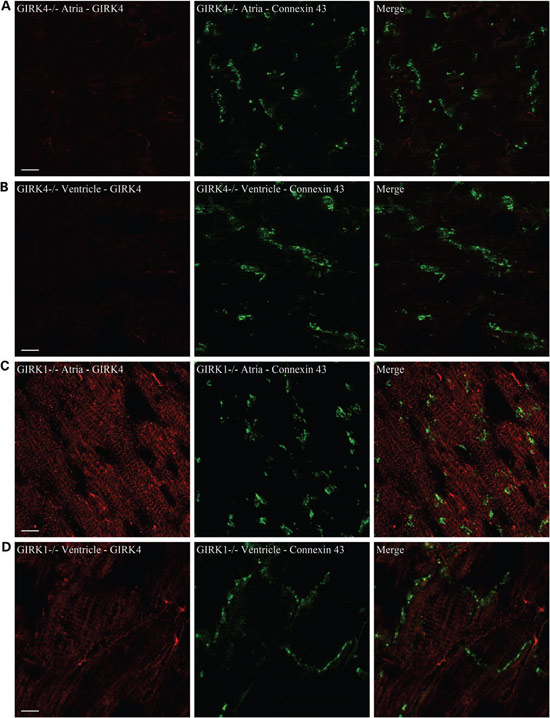
Knockout validation of Anti-KCNJ5 (Kir3.4) Antibody in mouse heart.
Immunohistochemical staining of mice heart using Anti-KCNJ5 (Kir3.4) Antibody (#APC-027). A. GIRK4 staining in GIRK4 KO mice atrial sections. B. GIRK4 staining in GIRK4 KO mice ventricular sections. C. GIRK4 staining in GIRK1 KO mice atrial sections and (D) ventricular sections. Staining demonstrates that the channel is localized to the outer sarcolemma and the ventricular t-tubular system. Scale bar = 10 μm.
Adapted from Liang, B. et al. (2014) with permission of the European Society of Cardiology.
