Overview
- Peptide HDVLEVKRKYYKVNC, corresponding to amino acid residues 311-325 of rat KCNJ16 (Accession P52191). Intracellular, C-terminal.

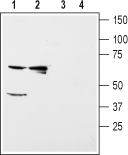 Western blot analysis of rat kidney (lanes 1 and 3) and liver (lanes 2 and 4) membranes:1,2. Anti-Kir5.1 Antibody (#APC-123), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat kidney (lanes 1 and 3) and liver (lanes 2 and 4) membranes:1,2. Anti-Kir5.1 Antibody (#APC-123), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Kir5.1 Antibody, preincubated with Kir5.1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC123). Western blot analysis of mouse brain (lanes 1 and 3) and kidney (lanes 2 and 4) membranes:1,2. Anti-Kir5.1 Antibody (#APC-123), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain (lanes 1 and 3) and kidney (lanes 2 and 4) membranes:1,2. Anti-Kir5.1 Antibody (#APC-123), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Kir5.1 Antibody, preincubated with Kir5.1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC123).
 Expression of Kir5.1 in rat kidneyImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin embedded section of rat kidney using Anti-Kir5.1 Antibody (#APC-123) (1:100). Kir5.1 (brown staining) is expressed in both proximal tubules (PT) and distal tubules (DT) in the renal cortex. Note that collecting ducts (CD) are less stained while glomeruli (G) are negative. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
Expression of Kir5.1 in rat kidneyImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin embedded section of rat kidney using Anti-Kir5.1 Antibody (#APC-123) (1:100). Kir5.1 (brown staining) is expressed in both proximal tubules (PT) and distal tubules (DT) in the renal cortex. Note that collecting ducts (CD) are less stained while glomeruli (G) are negative. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.- Human brain sections (1:500) (Schirmer, L. et al. (2014) Ann. Neurol. 75, 810.).
- Bond, C.T. et al. (1994) Rec. Channels 2, 183.
- Hebert, S.C. et al. (2005) Physiol. Rev. 85, 319.
- Tanemoto, M. et al. (2002) Neuron 34, 387.
Kir5.1 is a member of the family of inward rectifying K+ channels. The family includes 15 members that are structurally and functionally different from the voltage-dependent K+ channels.
The family’s protein topology consists of two transmembrane domains that flank a single and highly conserved pore region with intracellular N- and C-termini. As is the case for the voltage-dependent K+ channels the functional unit for the Kir channels is composed of four subunits that can assemble as either homo- or heteromers.
Kir channels are characterized by a K+ efflux that is limited by depolarizing membrane potentials thus making them essential for controlling resting membrane potential and K+ homeostasis.1
Kir5.1 can co-assemble with other Kir channels such as Kir2.1, Kir4.1 and Kir4.2. In fact, heteromeric Kir4.1/Kir5.1 form the basolateral small-conductance K+ channel in distal nephron segments that is responsible for generating the basolateral membrane potential that determines the magnitude and direction of K+ diffusion from cell to peritubular fluid in the nephron.2
The Kir5.1 homomeric channel was largely thought to be non-functional, although recent evidence demonstrates that Kir5.1 homomers can form functional channels when co-expressed with the anchor protein PSD-95 in the brain where it is abundantly expressed.3
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Kir5.1 Antibody (#APC-123) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize Kir5.1 from rat, mouse, and human samples.
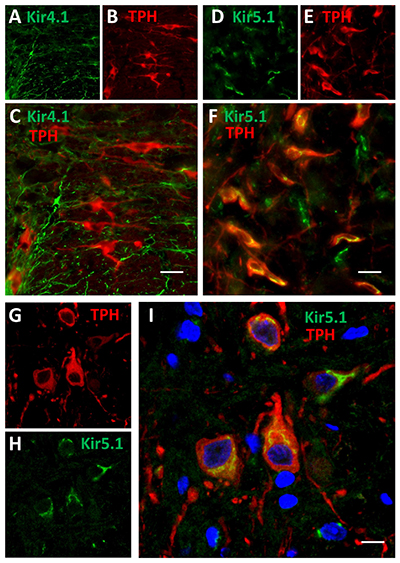 Expression of Kir4.1 and Kir5.1 channels in rat brainstem.Immunohistochemical staining of rat brainstem sections using Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody (#APC-035) and Anti-Kir5.1 Antibody (#APC-123) showed that both channels are expressed (green). Kir4.1 staining is limited to astrocytes, while that of Kir5.1 is detected in 5-HT neurons together with the 5-HT neuronal marker TPH (red).Adapted from Puissant, M.M. et al. (2017) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 11, 34. with permission of Frontiers.
Expression of Kir4.1 and Kir5.1 channels in rat brainstem.Immunohistochemical staining of rat brainstem sections using Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody (#APC-035) and Anti-Kir5.1 Antibody (#APC-123) showed that both channels are expressed (green). Kir4.1 staining is limited to astrocytes, while that of Kir5.1 is detected in 5-HT neurons together with the 5-HT neuronal marker TPH (red).Adapted from Puissant, M.M. et al. (2017) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 11, 34. with permission of Frontiers.Applications
Citations
- Rat brain lysate (1:100).
Puissant, M.M. et al. (2017) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 11, 34. - Mouse brain lysate (1:200).
Zhang, X. et al. (2011) Am. J. Physiol. 301, C729.
- Mouse brain sections.
Brasko, C. et al. (2017) Brain Struct. Funct. 222, 41. - Rat brainstem sections (1:1000).
Puissant, M.M. et al. (2017) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 11, 34. - Human brain sections (1:500).
Schirmer, L. et al. (2014) Ann. Neurol. 75, 810.
