Overview
- Peptide (C)KRNSMRRNNSMRRSN, corresponding to amino acid residues 382-396 of rat Kir6.1 (Accession Q63664). Intracellular, C-terminal part.
- Rat heart membranes and rat cortex lysate (1:200).
Human umbilical vein segment lysate (Protić, D. et al. (2014) Phytother. Res. 28, 1412.).  Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-Kir6.1 (KCNJ8) Antibody (#APC-105), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-Kir6.1 (KCNJ8) Antibody (#APC-105), (1:200).
2. Anti-Kir6.1 (KCNJ8) Antibody, preincubated with Kir6.1/KCNJ8 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC105).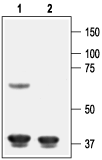 Western blot analysis of rat cortex lysate:1. Anti-Kir6.1 (KCNJ8) Antibody (#APC-105), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat cortex lysate:1. Anti-Kir6.1 (KCNJ8) Antibody (#APC-105), (1:200).
2. Anti-Kir6.1 (KCNJ8) Antibody, preincubated with Kir6.1/KCNJ8 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC105).
- Mouse heart lysate (Li, J. et al. (2010) J. Biol. Chem. 285, 28723.).
- Rat uterus sections (1:50).
Mouse brain sections (1:100) (Parsons, M.P. and Hirasawa, M. (2010) J. Neurosci. 30, 8061.).
Kir6.1 is a member of the inward rectifier K+ channels (Kir channels), a large family of voltage-independent K+ channels largely involved in stabilization of the membrane resting potential and in K+ transport across membranes.
Kir6.1, like its close relative Kir6.2, is highly sensitive to inhibition by intracellular ATP. Closure of the channel leads to membrane depolarization thereby coupling intracellular metabolism to cellular excitability.
Kir6.1 presents the common topology of the inward-rectifier superfamily: two transmembrane domains flanking a highly conserved pore region with the N- and C-termini located intracellularly.
The functional ATP sensitive channel (KATP) is composed of octamers of four Kir6.x subunits and four members of the sulfonylurea receptor family SUR1, SUR2A and SUR2B.
The channel's tissue distribution is relatively broad with expression detected in heart, brain, and smooth muscle.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
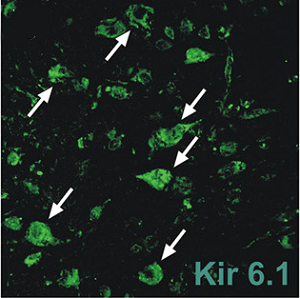 Expression of Kir6.1 in mouse brain sections.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Anti-Kir6.1 (KCNJ8) Antibody (#APC-105). Kir6.1 staining (green) is detected and coincides with orexin neurons.Adapted from Parsons, M.P. and Hirasawa, M. (2010) J. Neurosci. 30, 8061. with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.
Expression of Kir6.1 in mouse brain sections.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Anti-Kir6.1 (KCNJ8) Antibody (#APC-105). Kir6.1 staining (green) is detected and coincides with orexin neurons.Adapted from Parsons, M.P. and Hirasawa, M. (2010) J. Neurosci. 30, 8061. with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.
