Overview
- Peptide (C)SVAVAKAKPKFSIS, corresponding to amino acid residues 372-385 of rat Kir6.2 (Accession P70673). Intracellular, C-terminal part.
- Rat pancreas lysate (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of rat pancreas membranes:1. Anti-Kir6.2 Antibody (#APC-020), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat pancreas membranes:1. Anti-Kir6.2 Antibody (#APC-020), (1:200).
2. Anti-Kir6.2 Antibody, preincubated with Kir6.2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC020).
- Mouse heart lysate (Li, J. et al. (2010) J. Biol. Chem. 285, 28723.).
- Mouse ciliary cells (1:100) (Ohba, T. et al. (2013) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 347, 145.)
Mouse endothelial cells. Also tested in Kir6.2-/- mice (Milovanova, T. et al. (2005) Am. J. Physiol. 290, C66.).
Kir6.2 is a member of the inward rectifier K+ channels (Kir channels), a large family of voltage-independent K+ channels largely involved in stabilization of the membrane resting potential and in K+ transport across membranes. Kir channels can be modulated by a variety of intracellular agents such as protons, GTP-binding proteins and adenine nucleotides.
The ATP-sensitive channel (KATP) is especially important since it couples cellular metabolism (intracellular ATP levels) with cell excitability. KATP channels have been described in pancreatic b-cells, neurons, heart, skeletal and smooth muscle.
The KATP channel is composed of a Kir6.2 or Kir6.1 subunit and a sulphonylurea receptor (SUR) subunit.
The pancreatic KATP channel for example, is composed of a complex of Kir6.2 and SUR1 subunits, while the cardiac KATP channel is composed of Kir6.2 and SUR2A complexes.
Impaired b-cell KATP channel function due to mutations in either Kir6.2 or SUR1 subunits has been linked to the recessive autosomal disorder called persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy (PHHI). In addition, a Kir6.2 variant has recently been linked to an increased risk of developing type-2 diabetes.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
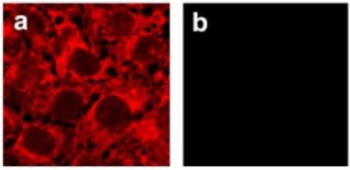
Knockout validation of Anti-Kir6.2 Antibody in mouse endothelial cells.Immunocytochemical staining of mouse endothelial cells using Anti-Kir6.2 Antibody (#APC-020). A. Kir6.2 staining (red) in wild type cells. B. Kir6.2 immunoreactivity is not detected in Kir6.2-/- cells.Adapted from Milovanova, T. et al. (2005) Am. J. Physiol. 290, C66. with permission of The American Physiological Society.
