Overview
- Peptide (C)EMNGDLEIDHDVPPE, corresponding to amino acid residues 80-94 of rat KCNJ13 (Accession O70617). Extracellular loop.

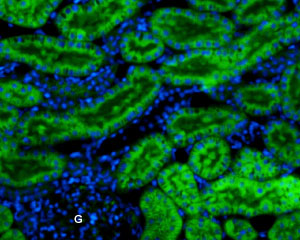 Expression of Kir7.1 in rat kidneyImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded rat kidney sections using Anti-Kir7.1 (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#APC-125-AG), (1:50). Kir7.1 staining (green) is present in convoluted tubules in the renal cortex. Glomeruli (G) are negative. Cell nuclei were visualized with Hoechst 33342 (blue).
Expression of Kir7.1 in rat kidneyImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded rat kidney sections using Anti-Kir7.1 (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#APC-125-AG), (1:50). Kir7.1 staining (green) is present in convoluted tubules in the renal cortex. Glomeruli (G) are negative. Cell nuclei were visualized with Hoechst 33342 (blue).
- Bond, C.T. et al. (1994) Rec. Channels 2, 183.
- Yang, D. et al. (2008) Exp. Eye Res. 86, 81.
- Hejtmancik, J.F. et al. (2008) Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82, 174.
Kir7.1 (KCNJ13) is a member of the inward rectifying K+ channel family. The family includes 15 members that are structurally and functionally different from the voltage-dependent K+ channels.
The family’s protein topology consists of two transmembrane domains that flank a single and highly conserved pore region with intracellular N- and C-termini. As is the case for the voltage-dependent K+ channels the functional unit for the Kir channels is composed of four subunits that can assemble as either homo- or heteromers.
Kir channels are characterized by a K+ efflux that is limited by depolarizing membrane potentials thus making them essential for controlling resting membrane potential and K+ homeostasis1.
Kir7.1, an inwardly rectifying K+ channel with unusual permeation properties is localized in epithelial cells of the thyroid, small intestine, kidney tubules, choroid plexus and in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), where it forms a major component of the apical membrane K+ conductance2.
A mutation in the gene encoding the channel was found to cause snowflake vitreoretinal degeneration (SVD) which is a developmental and progressive hereditary eye disorder that affects multiple tissues within the eye3.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Kir7.1 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-125) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and indirect flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize Kir7.1 from rat, mouse and human samples.
Anti-Kir7.1 (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#APC-125-AG) is directly labeled with an ATTO-488 fluorescent dye. ATTO dyes are characterized by strong absorption (high extinction coefficient), high fluorescence quantum yield, and high photo-stability. The ATTO-488 label is analogous to the well known dye fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and can be used with filters typically used to detect FITC. Anti-Kir7.1 (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody is especially suited for experiments requiring simultaneous labeling of different markers.
