Overview
- Peptide KDYPASTSQDSFEA(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 263-276 of human KV1.3 (Accession P22001). Extracellular loop between domains S1 and S2.

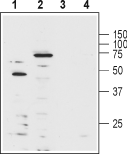 Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T cell leukemia cell lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-KV1.3 (KCNA3) (extracellular)-Biotin Antibody (#APC-101-B), (1:1000).
Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T cell leukemia cell lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-KV1.3 (KCNA3) (extracellular)-Biotin Antibody (#APC-101-B), (1:1000).
3-4. Anti-KV1.3 (KCNA3) (extracellular)-Biotin Antibody, preincubated with Kv1.3/KCNA3 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC101).
 Multiplex staining of KV1.3 and KV1.5 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse perfusion-fixed frozen brain sections using Anti-KV1.3 (KCNA3) (extracellular)-Biotin Antibody (#APC-101-B) (1:400), and Anti-KV1.5 (KCNA5)-ATTO Fluor-550 Antibody (#APC-004-AO), (1:60). A. KV1.3 staining (green) is detected in Bergmann glia soma and processes in the molecular layer (Mol) (arrow). B. Same section shows staining for KV1.5 (red). C. Merge of the two images suggests considerable co-localization in the soma of Bergmann glia. In the molecular layer, the distribution of KV1.5 is diffuse, unlike the discrete staining for KV1.3 in glial processes. Cell nuclei were visualized with DAPI (blue).
Multiplex staining of KV1.3 and KV1.5 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse perfusion-fixed frozen brain sections using Anti-KV1.3 (KCNA3) (extracellular)-Biotin Antibody (#APC-101-B) (1:400), and Anti-KV1.5 (KCNA5)-ATTO Fluor-550 Antibody (#APC-004-AO), (1:60). A. KV1.3 staining (green) is detected in Bergmann glia soma and processes in the molecular layer (Mol) (arrow). B. Same section shows staining for KV1.5 (red). C. Merge of the two images suggests considerable co-localization in the soma of Bergmann glia. In the molecular layer, the distribution of KV1.5 is diffuse, unlike the discrete staining for KV1.3 in glial processes. Cell nuclei were visualized with DAPI (blue).
- Chandy, K.G. et al. (2001) Toxicon 39, 1269.
- Koo, G.C. et al. (1997) J. Immunol. 158, 5120.
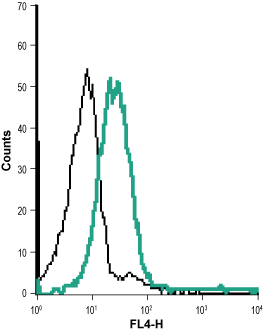
KV1.3 belongs to the Shaker family of voltage-dependent K+ channels. The channel, encoded by KCNA3, is widely expressed in the brain, lung and osteoclasts and in several cell populations of hematopoietic origin. The prominence of KV1.3 channels in these cells (particularly in T lymphocytes) directed much research attention. It was found that KV1.3 is the main channel responsible for maintaining the resting potential in quiescent cells and regulating the Ca2+ signaling that is indispensable for normal T lymphocyte activation.1,2 Based on the central role of KV1.3 in regulating the initiation of an immune response, the channel has been recognized as a potential target for immunosuppressant drugs.1 The central role of KV1.3 in immune system cells created a real need for a specific antibody that would be able to work in flow cytometry applications.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-KV1.3 (KCNA3) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-101) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, live cell imaging, and indirect flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize KV1.3 potassium channel from human, mouse, and rat samples.
Anti-KV1.3 (KCNA3) (extracellular)-Biotin Antibody (#APC-101-B) is directly labeled with biotin. Strepavidin tagged with HRP or with a fluorescent probe can then be used to detect the protein. The biotin/strepavidin system is ideal for minimizing cross-reactivity when same species antibodies are simultaneously used. Anti-KV1.3 (KCNA3) (extracellular)-Biotin Antibody has been tested in western blot, immunohistochemistry and direct flow cytometry and is specially suited to experiments requiring simultaneous labeling of different markers.