Overview
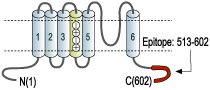
- GST fusion protein with the sequence HRETDHEEQAALKEEQGIQRRESGLDTGGQRKVSCSKASFHKTGGPLEST DSIRRGSCPLEKCHLKAKSNVDLRRSLYALCLDTS RETDL, corresponding to amino acid residues 513-602 of mouse KV1.5 (Accession Q61762). Intracellular, C-terminus.
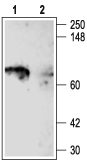 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-KV1.5 (KCNA5) Antibody (#APC-004), (1:100).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-KV1.5 (KCNA5) Antibody (#APC-004), (1:100).
2. Anti-KV1.5 (KCNA5) Antibody, preincubated with Kv1.5/KCNA5 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC004).- Human myeloid dendritic cells (1:500) (Zsiros, E. et al. (2009) J. Immunol. 183, 4483.).
- For examples see Product Citations.
- Rat brain sections (see also publications using this product).
Mouse heart sections (1 µg/ml) (Roepke, T.K. et al. (2008) FASEB J 22, 3648.).
- Rat cortical astrocytes (1:200) (MacFarlane, S.N. and Sontheimer, H. (2000) J. Neurosci. 20, 5245.).
- Swanson, R. et al. (1990) Neuron 4, 929.
- Gutman, G.A. et al. (2005) Pharmacol. Rev. 57, 473.
- McGahon, M.K. et al. (2007) Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 292, H1001.
KV1.5 is a mammalian voltage dependent K+ channel, homologous to the Drosophila Shaker K+ channel. KV1.5 was first cloned from the rat brain.1 Eight Shaker related genes exist in mammals constituting the KV1 subfamily of the large KV channel family of genes.2
A functional KV1 channel is either a membrane spanning homotetramer or heterotetramer, which is composed of members of the same subfamily. In addition several auxiliary subunits and intracellular proteins might interact with the channel and affect its function.
The structure of KV1.5 channel is similar to all KV channels and includes six membrane spanning helices creating a voltage sensor domain and a pore domain.2
The channel is expressed in cardiac and smooth muscle tissue (colon, aorta, stomach and pulmonary artery) as well as in neurons and kidney.2 A loss-of-function mutation in the gene encoding the channel was found in atrial fibrillation patients, stressing its role as a cardiac action potential regulator.3
The functional channel is considered transient (A-type) channel and shows prominent inactivation. Therefore, this channel activity influences the membrane potential and excitability of neurons and muscle.
KV1.5 channels are sensitive to high doses of TEA (330 mM) and low doses of 4-AP (0.27 mM), the “classical” non-selective potassium channel blockers.2
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-KV1.5 (KCNA5) Antibody (#APC-004) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, and immunoprecipitation applications. It has been designed to recognize KV1.5 from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Rat Neonatal ventricular myocyte lysate.
Milton, A.O. et al. (2020) J. Biol. Chem. 295, 4723. - Mouse heart lysates.
Kilfoil, P.J. et al. (2019) J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 137, 93. - Mouse heart lysate.
Tur, J. et al. (2016) Am. J. Physiol. 312, H571. - Mouse cardiac HL-1 cell lysate.
Lu, Y.Y. et al. (2016) J. Cell. Mol. Med. 20, 1182. - HEK 293 transfected cells.
Li, P. et al. (2015) J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 86, 138. - Mouse sarcolemmal protein lysate.
Ednie, A.R. and Bennett, E.S. (2015) J. Biol. Chem. 290, 2769. - Human lymphomas (1:500).
Vallejo Gracia, A. et al. (2013) J. Leukoc. Biol. 94, 779. - Mouse activated macrophages (BMDM cells).
Moreno, C. et al. (2013) J. Immunol. 191, 6136. - Rat lung lysate.
Lv, Y. et al. (2013) Am. J. Physiol. 305, L856. - Mouse heart lysate.
Huang, H. et al. (2013) J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 59, 151. - Human myeloid dendritic cells (1:500).
Zsiros, E. et al. (2009) J. Immunol. 183, 4483.
- HEK 293 transfected cells.
Li, P. et al. (2015) J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 86, 138.
- Human lymphomas (1:100).
Vallejo Gracia, A. et al. (2013) J. Leukoc. Biol. 94, 779. - Mouse heart sections (1 µg/ml).
Roepke, T.K. et al. (2008) FASEB J 22, 3648.
- HEK 293 transfected cells.
Jimenez-Perez, L. et al. (2016) J. Biol. Chem. 291, 3569. - HEK 293 transfected cells.
Li, P. et al. (2015) J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 86, 138. - Mouse leukaemia monocyte macrophage cells (raw 264.7), human Jurkat T-cells, human Raji B-lymphocytes .
Vallejo Gracia, A. et al. (2013) J. Leukoc. Biol. 94, 779. - Rat cortical astrocytes (1:200).
MacFarlane, S.N. and Sontheimer, H. (2000) J. Neurosci. 20, 5245.
- Christophersen, I.E. et al. (2013) Eur. Heart J. 34, 1517.
- Chen, W.L. et al. (2012) PLoS ONE 7, e49758.
- Chung, Y.H. et al. (2000) Brain Res. 875, 164.
- Maruoka, N.D. et al. (2000) FEBS Letters 473, 188.
- Peretz, A. et al. (2000) The EMBO J. 19, 4036.
- Yamashita, T. et al. (2000) Circulation 101, 2007.
- Clement-Chomienne, O. et al. (1999) J. Physiol. 515.3, 653.
- Hu, X.Q. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 5337.
- Sobko, A. et al. (1998) J. Neuroscience 18, 10398.
- Sobko, A. et al. (1998) EMBO J. 17, 4723.
- Guo, W. et al. (1997) Am. J. Physiol. 272, H2599.
- Guo, W. et al. (1997) Eur. J. Physiol. 434, 206.
