Overview
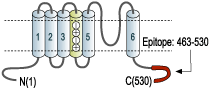
- GST fusion protein with the sequence NYFYHRETEQEEQGQYTHVTCGQPTPDLKATDNGLGKPDFAEASRERRSSYLPTPHRAYAEKRMLTEV, corresponding to amino acid residues 463-530 of rat KV1.6 (Accession P17659). Intracellular, C-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-KV1.6 (KCNA6) Antibody (#APC-003), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-KV1.6 (KCNA6) Antibody (#APC-003), (1:200).
2. Anti-KV1.6 (KCNA6) Antibody, preincubated with Kv1.6/KCNA6 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC003).
- Rat brain sections (see also 1,2 in publications using this product). Mouse cerebellum (1:350) (Kleopa, K.A. et al. (2006) Brain 129, 1570.).
- HeLa transfected cells (1:200) (Kleopa, K.A. et al. (2006) Brain 129, 1570.).
- Grupe, A. et al. (1990) EMBO J. 9, 1749.
- Gutman, G.A. et al. (2005) Pharmacol. Rev. 57, 473.
- Bogin, O. (2006) Modulator 21, 28.
KV1.6 is a mammalian voltage-dependent K+ channel, homologous to the Drosophila Shaker K+ channel. KV1.6 was first cloned from human brain.1 Eight Shaker-related genes exist in mammals constituting the KV1 subfamily of the large KV channel family of genes.2
A functional KV1 channel is either a membrane spanning homotetramer or heterotetramer, which is composed of members of the same subfamily. In addition several auxiliary subunits and intracellular proteins might interact with the channel and affect its function.
The structure of KV1.6 channel is similar to all KV channels and includes six membrane spanning helices creating a voltage sensor domain and a pore domain.2
The channel is expressed in neurons and other supporting cells in the brain, in cardiac and smooth muscle tissue as well as in ovary and testis2 and its activity influences the membrane potential and excitability of expressing cells.
KV1.6 channels are sensitive to low doses of TEA (7 mM) and high doses of 4-AP (1.5 mM), the “classical” non-selective potassium channel blockers.
Several toxins from snakes, scorpions and sea anemones venoms are potent blockers (affecting the channels in the nanomolar range) of KV1.6 channels. Among these the most potent and selective are α-Dendrotoxin ((9-25 nM) and δ-Dendrotoxin (23 nM), Agitoxin-2 (0.036 nM), Hongotoxin-1 (6 nM), Margatoxin (5 nM) and Stichodactyla Toxin (0.16 nM).3
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat KV1.6 channel. Anti-KV1.6 (KCNA6) Antibody (#APC-003) can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize KV1.6 from human, rat and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Mouse brain sections (1:400).
Blosa, M. et al. (2015) J. Physiol. 593, 4341. - Human artery tissues (1:50).
Gojkovic-Bukarica, L. et al. (2011) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 654, 266.
- Hao, J. et al. (2013) Neuron 77, 899.
- Kleopa, K.A. et al. (2006) Brain 129, 1570.
- Chittajallu, R. et. al. (2002) PNAS 99, 2350.
- Chung, Y.H. et al. (2000) Brain Res. 875, 164.
- Smart, S.L. et al. (1997) Glia 20, 127.
