Overview
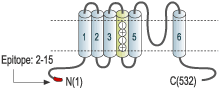
- Peptide TTRKAQEIHGKAPG(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 2-15 of mouse KV1.7 (Accession Q17ST2). Intracellular, N-terminus.
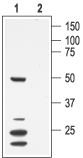 Western blot analysis of mouse heart membranes:1. Anti-Mouse KV1.7 (KCNA7) Antibody (#APC-063), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse heart membranes:1. Anti-Mouse KV1.7 (KCNA7) Antibody (#APC-063), (1:200).
2. Anti-Mouse KV1.7 (KCNA7) Antibody, preincubated with Mouse Kv1.7/KCNA7 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC063).
- Kalman, K. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 5851.
- Kashuba, V.I. et al. (2001) Gene 268, 115.
- Bardien-Kruger, S. et al. (2002) Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 10, 36.
The KV1.7 voltage-gated K+ channel, is a member of the Shaker family of K+ channels that today includes eight members (KV1.1-KV1.8). KV1.7 possesses the signature structure of the voltage-dependent K+ channels: six membrane-spanning domains and intracellular N- and C-termini. As with other channels of the Shaker subfamily, KV1.7 can readily form heteromers with other members of the subfamily to compose the tetramer that forms the functional channel.
KV1.7 mRNA was found to be expressed mainly in the heart with somewhat lower levels in pancreas and skeletal muscle.
The biophysical and pharmacological properties of the KV1.7 channel closely resembles that of the ultra-rapidly activating delayed rectifier (IKur) in cardiac tissue. This current plays a central role in cardiac atrial repolarization that was largely believed to correspond to the activity of the KV1.5 channel. This raises the possibility that the IKur current is the result of a heteromeric KV1.5/KV1.7 channel.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Mouse KV1.7 (KCNA7) Antibody (#APC-063) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot analysis. It has been designed to recognize KV1.7 from mouse samples. The antibody will not recognize the protein from human or rat samples.
