Overview
- Peptide (C)TPQHHISLKESTAK, corresponding to amino acid residues 54-67 of rat KCNAB1 (Accession P63144). N-terminus.

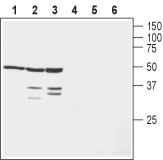 Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and rat brain lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-KVβ1 Antibody (#APC-127), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and rat brain lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-KVβ1 Antibody (#APC-127), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-KVβ1 Antibody, preincubated with Kvβ1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC127).
- Hille, B. (1992) Sinauer, Sunderland, MA.
- Zagotta, W.N. et al. (1990) Science 250, 56.
- Pongs, O. et al. (1999) Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 868, 344.
- McCormack, K. et al. (1995) FEBS Lett. 370, 32.
Voltage-gated K+ channels represent a structurally and functionally diverse group of membrane proteins. These channels establish the resting membrane potential and modulate the frequency and duration of action potentials in nerve and muscle1. The duration of the open states of K+ channels is determined by the rates of deactivation and inactivation. KV channels are hetero-oligomeric complexes consisting of two different types of subunits: membrane-bound, pore-forming α subunits and the smaller β subunits. The β subunits appear to be peripheral proteins tightly associated with the cytoplasmic side of the α subunits2.
The inactivation gate can be formed by an N-terminal segment of an auxiliary β-subunit, as in the complex of KVβ1 and KVα family channels3. There are three mammalian KVβ genes: KVβ1, KVβ2 and KVβ3. Additional variability in the KVβ1 family results from alternative splicing in the amino terminal region, thus yielding the KVβ1.1, KVβ1.2, and KVβ1.3 subunits4.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of rat KVβ1. Anti-KVβ1 Antibody (#APC-127) can be used in western blot analysis. This antibody will recognize the splice isoform of human KVβ1 (also known as KVβ1.1). It won’t recognize splice variants KVβ1.2 and KVβ1.3. For more information, see human KVβ1 entry Q14722 and Q14722-2. It has been designed to recognize KVβ1 from rat, mouse and human samples.
