Overview
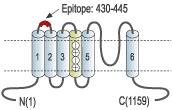
- Peptide AFLLKETEEGPPATEC corresponding to residues 430-445 of human KV11.1 (HERG) (Accession Q12809). Extracellular, between S1 and S2 domains.
 Western blot analysis of KV11.1 (HERG)-transfected HEK-293 cells:1. Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-109), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of KV11.1 (HERG)-transfected HEK-293 cells:1. Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-109), (1:200).
2. Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with KCNH2/HERG (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC109).
 Immunoprecipitation of KV11.1-expressing HEK-293 cells:1. Cell lysate.
Immunoprecipitation of KV11.1-expressing HEK-293 cells:1. Cell lysate.
2. Cell lysate + protein A beads + Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-109).
3. Cell lysate + protein A beads + Anti-KCNH2 (erg1) Antibody (#APC-016).
4. Cell lysate + protein A beads + Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) Antibody (#APC-062).
5. Cell lysate + protein A beads + pre-immune rabbit serum.
Red arrow indicates KV11.1 while the black arrow shows the IgG heavy chain.
Immunoblot was performed with Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody.
 Expression of KV11.1 (HERG) in rat heartImmunohistochemical staining of rat heart using Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-109). A. Transversal section of the atrium wall; note that arterial smooth muscle fibers were not stained (green arrow). B. Longitudinal section of the myocardium. C. Section showing myocardium and endocardium (red arrow). DAB product is brown and the counterstain is cresyl violet.
Expression of KV11.1 (HERG) in rat heartImmunohistochemical staining of rat heart using Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-109). A. Transversal section of the atrium wall; note that arterial smooth muscle fibers were not stained (green arrow). B. Longitudinal section of the myocardium. C. Section showing myocardium and endocardium (red arrow). DAB product is brown and the counterstain is cresyl violet.
 Cell surface detection of KV11.1 (HERG) by indirect flow cytometry in live intact human chronic myelogenous leukemia (K562) cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of KV11.1 (HERG) by indirect flow cytometry in live intact human chronic myelogenous leukemia (K562) cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + goat-anti-rabbit-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-109), (2.5μg) + goat-anti-rabbit-FITC.- The blocking peptide is not suitable for this application.
 Expression of KV11.1 (HERG) in HEK-293 transfected cellsCell surface detection of KV11.1 in live intact HEK-293 transfected cells. Cells were stained with Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-109), (1:25) (left panel) or with Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody preincubated with the blocking peptide (right panel), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-555 secondary antibody (red). Nuclei of the living cells were stained with the cell permeable dye Hoechst 33342 (blue). Note that not all cells are stained, indicating that not all the KV11.1 channels are expressed at the cell membrane at the moment of staining.
Expression of KV11.1 (HERG) in HEK-293 transfected cellsCell surface detection of KV11.1 in live intact HEK-293 transfected cells. Cells were stained with Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-109), (1:25) (left panel) or with Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody preincubated with the blocking peptide (right panel), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-555 secondary antibody (red). Nuclei of the living cells were stained with the cell permeable dye Hoechst 33342 (blue). Note that not all cells are stained, indicating that not all the KV11.1 channels are expressed at the cell membrane at the moment of staining.
- Curran, M.E. et al. (1995) Cell 80, 795.
- Sanguinetti, M.C. et al. (1995) Cell 81, 299.
- Pardo, L.A. et al. (2004) Physiology 19, 285.
The KV11.1 (HERG) channel is a member of the ether-a-go-go (EAG) subfamily of voltage-dependent K+ channels that includes the related proteins KV11.2 and KV11.3 (erg2 and erg3). KV11.1 possesses the signature structure of the voltage-dependent K+ channels: six membrane-spanning domains and intracellular N- and C-termini.
The KV11.1 current is characterized by strong inward rectification with slow activation and very rapid inactivation kinetics. The channel is expressed in the brain and heart (where it underlies the IKr current) and has a central role in mediating repolarization of action potentials.1,2
Mutations in the KV11.1 channel cause inherited long QT syndrome (LQTS) or abnormalities in the repolarization of the heart that are associated with life-threatening arrhythmias and sudden death. All the identified KV11.1 mutations produce loss of function of the channel via several cellular mechanisms ranging from alterations of gating properties, alterations of channel permeability/selectivity and alterations in intracellular channel trafficking that decreases the number of channels that reach the cell membrane.1,2
Recently, drug-induced forms of LQTS have been reported for a wide range of non-cardiac drugs including antihistamines, psychoactive agents and antimicrobials. All these drugs potently block the KV11.1 channel as an unintended side effect, prompting regulatory drug agencies to issue recommendations for the testing of new drugs for their potential KV11.1 blocking effect.
In addition, KV11.1 expression was found to be upregulated in several tumor cell lines of different histogenesis, suggesting that it confers the cells some advantage in cell proliferation. Indeed, in several studies it has been shown that inhibition of the KV11.1 current leads to a decrease in tumor cell proliferation.3
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-KCNH2 (HERG) (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-109) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the human KV11.1 channel. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunoprecipitation, immunohistochemical, immunocytochemical and indirect flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize KV11.1 from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Crottes, D. et al. (2011) J. Biol. Chem. 286, 27947.
- Mihic, A. et al. (2011) PLoS One. 6, e18273.
- Smith, J.L. et al. (2011) Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 301, C75.
- Stump, M.P. et al. (2011) Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 300, H312.
- Wu, Z-Y. et al. (2011) J. Biol. Chem. 286, 22186.
- Nof, E. et al. (2010) Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet 3, 199.
- Delisle, B.P. et al. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 2844.
- Potet, F. et al. (2009) J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 46, 257.
- Chtcheglova, L.A. et al. (2008) Pflugers Arch. 456, 247.
- Claassen, S. et al. (2008) J. Membr. Biol. 222, 31.
- Takemasa, H. et al. (2008) Br. J. Pharmacol. 153, 439.
- Wu, Z-Y. et al. (2008) Endocrinology 149, 5061.
