Overview
- Peptide (C)HMLPGGGAHGSTRDQSI, corresponding to amino acid residues 841-857 of rat KV2.1 (Accession P15387). Intracellular, C-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Guinea pig Anti-KV2.1 Antibody (#APC-012-GP), (1:500).
Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Guinea pig Anti-KV2.1 Antibody (#APC-012-GP), (1:500).
3,4. Guinea pig Anti-KV2.1 Antibody, preincubated with Kv2.1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC012).
 Expression of KV2.1 channel in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of rat hippocampal CA1 region using Guinea pig Anti-KV2.1 Antibody (#APC-012-GP), (1:400). A. KV2.1 staining (green) appears in the pyramidal layer (P) and in stratum oriens (SO) interneurons (horizontal arrows). B. Nuclei staining using DAPI as the counterstain (blue). C. Merged image of panels A and B.
Expression of KV2.1 channel in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of rat hippocampal CA1 region using Guinea pig Anti-KV2.1 Antibody (#APC-012-GP), (1:400). A. KV2.1 staining (green) appears in the pyramidal layer (P) and in stratum oriens (SO) interneurons (horizontal arrows). B. Nuclei staining using DAPI as the counterstain (blue). C. Merged image of panels A and B.
- Wulff, H. et al. (2009) Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 8, 982.
- Thiffault, I. et al. (2015) J. Gen. Physiol. 146, 399.
Voltage gated K+ channels are involved in diverse physiological processes ranging from repolarization of neuronal and cardiac action potential, regulation of Ca2+ signaling and cell volume to driving cellular proliferation and migration.
KV2.1 consists of four α-subunits, each containing six transmembrane α-helical segments, S1-S6, and a membrane-re-entering P-loop, which are arranged circumferentially around a central pore. This ion conduction pore is lined by four S5-P-S6 sequences. The four first segments(1-4), each containing four positively charged arginine residues in the Segment number 4 helix, act as voltage sensor domains and “gate” the pore by “pulling” on the segments 4 and 5 linker.
KV2.1, encoded by the KCNB1 gene, is a classical delayed rectifier channel that is involved in neuronal repolarization. Its function can be diversified through heteromultimerization with “silent” KV units, which modify inactivation, trafficking, drug sensitivity and expression.
Inhibition of KV2.1 in pancreatic β-cells enhances insulin secretion, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy for type 2 diabetes. This effect is presumed to occur through non-conducting functions - namely, a physical interaction with syntaxin (a component of the soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor complex) that facilitates vesicle fusion1.
Recently, a “de novo” pathogenic KV2.1 variant was discovered in a family suffering from idiopathic epileptic encephalopathy. This variant is a missense mutation in the coding region of the KCNB1 gene. Expression of the V378A variant results in voltage-activated currents that are sensitive to the selective KV2 channel blocker guangxitoxin-1E. Currents through the mutant channel are non-selective among monovalent cations2.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Guinea pig Anti-KV2.1 Antibody (#APC-012-GP, formerly AGP-109) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize KV2.1 from mouse, rat, and human samples. The antigen used to immunize guinea pigs is the same as Anti-KV2.1 Antibody (#APC-012) raised in rabbit. Our line of guinea pig antibodies enables more flexibility with our products such as multiplex staining studies, immunoprecipitation, etc.
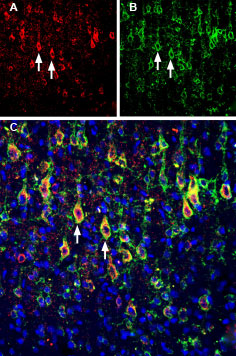 Multiplex staining of Slitrk1 and KV2.1 in rat parietal cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of immersion-fixed, free floating rat brain frozen sections using rabbit Anti-Slitrk1 extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-081), (1:200) and Guinea pig Anti-KV2.1 Antibody (#APC-012-GP), (1:200). A. Slitrk1 staining (red) appears in profiles of pyramidal neurons. B. KV2.1 staining (green) is detected in profiles of pyramidal neurons. C. Merge of the two images shows colocalization in several neurons (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Multiplex staining of Slitrk1 and KV2.1 in rat parietal cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of immersion-fixed, free floating rat brain frozen sections using rabbit Anti-Slitrk1 extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-081), (1:200) and Guinea pig Anti-KV2.1 Antibody (#APC-012-GP), (1:200). A. Slitrk1 staining (red) appears in profiles of pyramidal neurons. B. KV2.1 staining (green) is detected in profiles of pyramidal neurons. C. Merge of the two images shows colocalization in several neurons (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
