Overview
- Peptide SPGMIYSTRYGSPKR(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 20-34 of rat KCNAB2 (Accession P62483). N-terminal part.

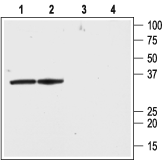 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-KVβ2 Antibody (#APC-117), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-KVβ2 Antibody (#APC-117), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-KVβ2 Antibody, preincubated with Kvβ2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC117). Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T cells:1. Anti-KVβ2 Antibody (#APC-117), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T cells:1. Anti-KVβ2 Antibody (#APC-117), (1:200).
2. Anti-KVβ2 Antibody, preincubated with Kvβ2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC117).
 Expression of KVβ2 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum using Anti-KVβ2 Antibody (#APC-117). A. KVβ2 appears adjacent to Purkinje cells (green). B. Staining of GABAergic cells with mouse anti-parvalbumin (PV, red). C. Confocal merge of KVβ2 and PV demonstrates the presence of KVβ2 adjacent to Purkinje cells.
Expression of KVβ2 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum using Anti-KVβ2 Antibody (#APC-117). A. KVβ2 appears adjacent to Purkinje cells (green). B. Staining of GABAergic cells with mouse anti-parvalbumin (PV, red). C. Confocal merge of KVβ2 and PV demonstrates the presence of KVβ2 adjacent to Purkinje cells.
- Rat hippocampus primary neurons (1:200) (Proepper, C. et al. (2014) Neuroscience 261, 133.).
- Parcej, D.N. et al. (1992) Biochemistry 31, 11084.
- Rettig, J. et al. (1994) Nature 369, 289.
- Pongs, O. et al. (1999) Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 868, 344.
- Li, Y. et al. (2006) Neuroscientist 12, 199.
KVβ2 (or KCNAB2) is a member of a family of proteins that regulate the activity of voltage-dependent K+ channels. The other members of the family are KVβ1 and KVβ3.
The KVβ subunits were originally identified using a biochemical approach that demonstrated that the ion-conducting α subunits existed in a macromolecular complex with auxiliary β subunits with a probable stoichiometry of α4β4. It is now widely established that the regulatory β subunits are able to alter both the biophysical (i.e. acceleration of inactivation kinetics) and biochemical (promote cell surface expression) properties of the functional KV channel.
The KVβ regulatory subunits are cytosolic proteins with conserved C-termini and variable N-terminus domains. The interaction with the α subunits is via the conserved C-terminus that binds to a specific sequence in the N-terminus of the α subunits.
KVβ2, as well as the other KVβ subunits can bind to all the members of the large KV1.x (Shaker) channel subfamily. However, recent evidence suggests that it can also bind to members of the KV4.x subfamily.
KVβ2 is the most abundant β subunit in the brain, where it couples with all the KV1.x subunits, but the protein is also expressed in peripheral tissues including the heart, lungs and cells of hematopoietic origin such as T cells where it couples with KV1.3, the dominant voltage-dependent K+ channel in these cells.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of rat KVβ2. Anti-KVβ2 Antibody (#APC-117) can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize KVβ2 from rat, mouse and human samples.
Applications
Citations
- Rat brain lysate (1:400).
Proepper, C. et al. (2014) Neuroscience 261, 133.
- Rat hippocampus primary neurons (1:200).
Proepper, C. et al. (2014) Neuroscience 261, 133.
- Jukkola, P.I. et al. (2012) Neurobiol. Dis. 47, 280.
- Zencker, J. et al. (2012) J. Neurosci. 32, 7493.
