Overview
- Peptide EAGDD ERELA LQRLG PHEG(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 177-195 of rat KCNC4 (Accession Q63734). Intracellular, N-terminal.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysates:1. Anti-KCNC4 (KV3.4) Antibody (#APC-019), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysates:1. Anti-KCNC4 (KV3.4) Antibody (#APC-019), (1:200).
2. Anti-KCNC4 (KV3.4) Antibody, preincubated with KCNC4/Kv3.4 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC019).
- Transfected COS-7 cells (10 μg antibody with 1.5 mg total protein) (Abbott, G.W. et al. (2001) Cell 104, 217.).
- Rat brain sections.
Mouse transversus abdominus (1:100-1:1000) (Brooke, R.E. et al. (2004) Eur. J. Neurosci. 20, 3313.).
- Rabbit carotid body (1:100) (Kaab, S. et al. (2004) J. Physiol. 566, 395.).
- Schroter, K.H. et al. (1991) FEBS Lett. 278, 211.
- Rettig, J. et al. (1992) EMBO J. 11, 2473.
- Abbott, G.W. et al. (2001) Cell 104, 217.
- Diochot, S. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 6744.
KV3.4 is a member of the voltage-gated K+ channel superfamily. Together with the related proteins KV3.1, KV3.2 and KV3.3 they constitute the Shaw type subfamily family.1
As with all Kv channels, KV3.4 possesses the signature structure of the voltage-dependent K+ channels: six membrane-spanning domains with intracellular N and C termini. The functional KV channel is a tetramer that can either be a homomer or a heteromer of KV3 subunits.2
Kv3 subfamily members inactivate very rapidly and therefore are thought to play a role in the repolarization of action potentials and to facilitate repetitive high frequency firing.2
Kv3.4 expression is wide and the channel can be found in brain, skeletal muscle, prostate and pancreas among others.
KV3.4 subunits have been implicated recently in the response mechanism to chronic hypoxia and the etiology of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. In addition, KV3.4 was found to associate with the auxiliary subunit KCNE3 (MirP2) in skeletal muscle. A mutation in KCNE3 (R83H) has been associated with an inherited form of periodic paralysis (Thyrotoxic hypokalemic periodic paralysis) that is caused by the altered physiological function of the KV3.4 channel.3
Toxins from sea anemone, BDS-I (#STB-400), (47 nM) and BDS-II (#B-450), (56 nM), are potent blockers of KV3.4 channels.4
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-KCNC4 (KV3.4) Antibody (#APC-019) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunoprecipitation, immunocytochemistry, and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize KV3.4 from human, rat, and mouse samples.
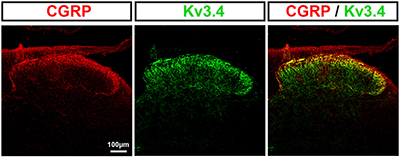
Expression of KV3.4 in rat dorsal horn.Immunohistochemical staining of rat spinal cord sections using Anti-KCNC4 (KV3.4) Antibody (#APC-019). KV3.4 staining (green) is observed in dorsal horn laminae I–III. KV3.4 immunoreactivity partially co-localizes with CGRP (red).Adapted from Muqeem, T. et al. (2018) J. Neurosci. 38, 3729. with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.
Applications
Citations
 Decrease in KV3.4 cell surface expression following SCI.Immunohistochemical staining of rat dorsal root ganglion following laminectomy (upper panels) and spinal cord injury (SCI) (lower panels) using Anti-KCNC4 (KV3.4) Antibody (#APC-019). KV3.4 surface expression (green) decreases following SCI as opposed to laminectomy.
Decrease in KV3.4 cell surface expression following SCI.Immunohistochemical staining of rat dorsal root ganglion following laminectomy (upper panels) and spinal cord injury (SCI) (lower panels) using Anti-KCNC4 (KV3.4) Antibody (#APC-019). KV3.4 surface expression (green) decreases following SCI as opposed to laminectomy.
Adaped from Ritter, D.M. et al. (2015) with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.
- Transfected COS-7 cells (10 μg antibody with 1.5 mg total protein).
Abbott, G.W. et al. (2001) Cell 104, 217.
- Rat brain sections.
Muqeem, T. et al. (2018) J. Neurosci. 38, 3729. - Rat lumbar spinal cord sections.
Wolff, M. et al. (2016) Neurosci. Res. 109, 16. - Rat DRG sections (1:1000).
Ritter, D.M. et al. (2015) J. Neurosci. 35, 1260. - Mouse transversus abdominus (1:100-1:1000).
Brooke, R.E. et al. (2004) Eur. J. Neurosci. 20, 3313.
- Rabbit carotid body (1:100).
Kaab, S. et al. (2004) J. Physiol. 566, 395.
- Gopel, S.O. et al. (2000) J. Physiol. 528.3, 497.
