Overview
- Peptide (C)NEALELTGTPEEEHMGK, corresponding to amino acid residues 451-468 of human KV4.3 (Accession O60577). Intracellular, C-terminus.
- Rat brain membranes (1:200). Human heart lysate (1:250) (Zicha, S. et al. (2004) J. Physiol. 561, 735.).
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-KV4.3 Antibody (#APC-017), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-KV4.3 Antibody (#APC-017), (1:200).
2. Anti-KV4.3 Antibody, preincubated with Kv4.3 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC017).
- Canine heart lysate (5 μg) (Doronin, S.V. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 48231.).
- HEK-293 transfected cells (1:50) (Hatano, N. et al. (2002) Pflugers Arch. 444, 80.).
KV4.3 is a voltage-dependent K+ channel that belongs to the Shal channel subfamily and includes two other members: KV4.1 and KV4.2.
KV4.3 possesses the signature structure of the voltage-dependent K+ channels; six membrane-spanning domains with intracellular N and C termini. As with other members of the voltage-gated K+ channel superfamily, the functional channel is a tetramer that can be composed of more than one member of the Shal subfamily, i.e. heterotetramers of KV4.1 and KV4.2.
The KV4 channels are characterized by activation at subthreshold membrane potentials, rapid inactivation and fast recovery from inactivation compared with other voltage-dependent K+ channels. This type of current is known as transient A-type K+ currents.1
The biophysical properties of the KV4.3 subunit can be modified by its association with auxiliary β subunits such as the KChIP family that increases current densities and accelerates both the inactivation and the recovery time.
KV4.3 is highly expressed in the brain where it has a key role in shaping the action potential and firing frequency of neurons. In the heart, together with KV4.2, it underlies the fast inactivating and recovering cardiac transient outward current Ito.2,3 The channel is also expressed in smooth muscle cells of several organs such as myometrium, lung and colon where its function has not been completely elucidated.
Several toxins from spider venoms are potent blockers (affecting the channels in the nanomolar range) of KV4.3 channels. Among these the most potent and selective are Phrixotoxin-1 (#STP-700) (28 nM) and Phrixotoxin-2 (#STP-710) (71 nM).4
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
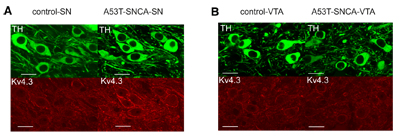 Expression of KV4.3 increases in DA substantia-nigra neurons of α-synuclein mutant mice but not in DA neurons in the ventral tegmental area.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Anti-KV4.3 Antibody (#APC-017). A. Expression of KV4.3 increases in DA substantia-nigra neurons of α-synuclein mutant mice (lower right panel). B. Expression of KV4.3 does not increase in DA neurons of the ventral tegmental area in α-synuclein mutant mice (lower right panel).Adapted from Subramaniam, M. et al. (2014) with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.
Expression of KV4.3 increases in DA substantia-nigra neurons of α-synuclein mutant mice but not in DA neurons in the ventral tegmental area.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Anti-KV4.3 Antibody (#APC-017). A. Expression of KV4.3 increases in DA substantia-nigra neurons of α-synuclein mutant mice (lower right panel). B. Expression of KV4.3 does not increase in DA neurons of the ventral tegmental area in α-synuclein mutant mice (lower right panel).Adapted from Subramaniam, M. et al. (2014) with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.