Overview
- Peptide (C)TYEQLTVPRRGPDEGS, corresponding to amino acid residues 661-676 of human KCNQ1 (Accession P51787). Intracellular, C-terminus.
- Rat heart membranes (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-KCNQ1 Antibody (#APC-022), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-KCNQ1 Antibody (#APC-022), (1:200).
2. Anti-KCNQ1 Antibody, preincubated with KCNQ1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC022).
- Canine left ventricle (8 μg) (Ehrlich, J.R. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 1233.).
- Mouse distal colon (1:50) (Jepps, T.A. et al. (2009) Am. J. Physiol. 297, G107.).
- COS cells (Wiener, R. et al. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283, 5815.).
KCNQ1 (KV7.1) is part of a voltage-gated K+ family that includes 5 other members (KCNQ1-5).
The channel has been intensively studied since it was found that together with MinK (Isk) it underlay the cardiac Iks current that controls the duration of the action potential of the human heart. Indeed mutations on either KV7.1 or MinK can be responsible for long QT syndrome, a cardiac disorder that causes arrhythmias and sudden death.
Although KV7.1 expression and function has been mainly investigated in relation with cardiac function the channel is widely distributed in epithelial tissues. There it has been implicated in physiological functions such as the regulation of acid secretion in the stomach and Cl- secretion into the colon.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
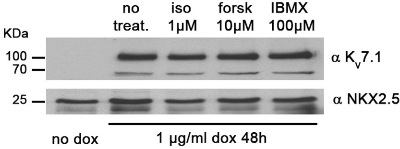 Expression of KCNQ1 (KV7.1) in hiPSC-CMs.Western blot analysis of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) under different treatments using Anti-KCNQ1 Antibody (#APC-022). Protein levels of KCNQ1 remain the same.Adapted from Piccini, I. et al. (2017) Front. Physiol. 8, 705. with permission of Frontiers.
Expression of KCNQ1 (KV7.1) in hiPSC-CMs.Western blot analysis of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) under different treatments using Anti-KCNQ1 Antibody (#APC-022). Protein levels of KCNQ1 remain the same.Adapted from Piccini, I. et al. (2017) Front. Physiol. 8, 705. with permission of Frontiers.
