Overview
- Peptide AEGEKKEDNRYSDLKTIIC, corresponding to amino acid residues 668-686 of rat KCNQ3 (Accession O88944). Intracellular, C-terminal.
- Rat brain membranes (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-KCNQ3 Antibody (#APC-051), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-KCNQ3 Antibody (#APC-051), (1:200).
2. Anti-KCNQ3 Antibody, preincubated with KCNQ3 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC051).
- Mouse cortical lysate (Ebner Bennatan, S. et al. (2012) J. Biol. Chem. 287, 27614.).
- Rat brain sections.
- Rat hippocampal neurons (1:100) (Rasmussen, H.B. et al. (2007) J. Cell Sci. 120, 953.).
The KCNQ family of voltage-gated K+ channels includes 5 known members: KCNQ1 to KCNQ5. Structurally, the KCNQ family belongs to the six transmembrane domain category of K+ channels. KCNQ family members can form either homomultimeric or heteromultimeric channels with different functional consequences. For example KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 heteromultimers give rise to a much larger channel current than when either protein is expressed alone, probably due to enhanced plasma membrane expression of the combined channel. Indeed, KCNQ2/KCNQ3 heteromultimers are believed to be the molecular correlates of the so-called M current. This current is a K+ neuronal current that is strongly inhibited by the activation of the M1 subtype of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor.
Mutations in either KCNQ2 or KCNQ3 are associated with a form of epilepsy known as benign familial neonatal convulsions (BFNC).
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
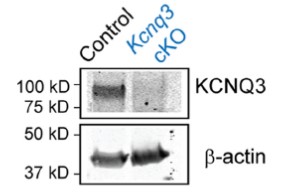
Knockout validation of Anti-KCNQ3 Antibody in mouse hippocampus.Western blot analysis of mouse hippocampus membrane fractions using Anti-KNQ3 Antibody (#APC-051), (upper panel). KCNQ3 immunodetection is observe in control mice (left lane) and absent in KCNQ3 conditional knockout mice (right lane). β-actin is used as a loading control.Adapted from Soh, H. et al. (2014) J. Neurosci. 34, 5311. with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.
